Hemangioendothelioma is a rare spectrum of vascular tumors with characteristics intermediate between those of benign, well-differentiated hemangiomas and aggressively malignant angiosarcomas.
What is the Pathology of Hemangioendothelioma?
The pathology of hemangioendothelioma is:
-Etiology: The cause of hemangioendothelioma is genetic factor.
-Genes involved: ERPINE1-FOSB gen.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hemangioendothelioma; the lesion arises in the lower limbs soft tissue and less often in the trunk and upper limbs. There is t(7;19)(q22;q13) chromosomal translocation causing SERPINE1-FOSB gene union in the recurrent alteration.
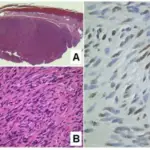
-Morphology: The morphology associated with hemangioendothelioma shows nodular masses.
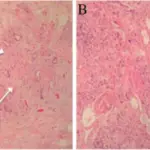
-Histology: The histology associated with hemangioendothelioma shows cells that are plump/cuboidal and not well-defined vascular channels.
How does Hemangioendothelioma Present?
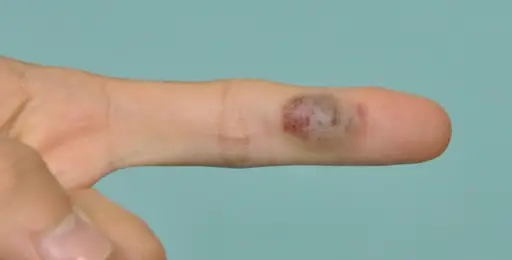
Patients with hemangioendothelioma typically have male predominance present at age range of 30 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hemangioendothelioma include pain, swelling round tumor, weight loss, walking difficulties, skin lumps, fever, and troubled breathing.
How is Hemangioendothelioma Diagnosed?
Hemangioendothelioma is diagnosed laboratory studies-biopsy. Imaging-CT scan, MRI, X-ray and PET scan.
How Hemangioendothelioma Treated?
Hemangioendothelioma is treated through surgical excision and radiotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Hemangioendothelioma?
The prognosis of hemangioendothelioma is fair.