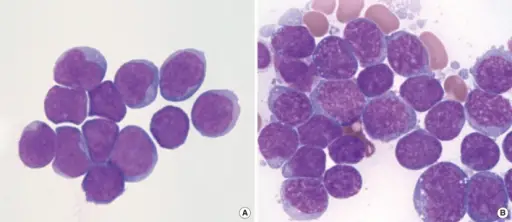
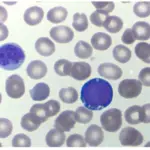
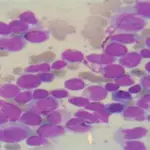
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) is an aggressive (fast-growing) type of leukemia (blood cancer) in which too many B-cell lymphoblasts (immature white blood cells) are found in the bone marrow and blood.
What is the Pathology of B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL)?
The pathology of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is unknown. Some things make this disease more likely, including exposure to high doses of X-rays and other forms of radiation, or cancer treatment with chemotherapy.
-Genes involved: PAX5, EBF1, IKZF1-3, lymphoid enhancer factor 1 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma involves a number of abnormal gene expressions (including TEL-AML1, BCR-ABL-1, RAS and PI3K) leading to dysregulated cell cycle.
-Histology: The histology associated with b-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma shows blasts that tend to have FAB L3 features, with intensely staining cytoplasmic basophilia similar to that of erythroblasts.
How does B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) Present?
Patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma typically are males (1.84:1 male to female ratio) present at age range of <15 years with a second peak of incidence around 40 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma include anemia, loss of appetite, fever, fatigue, bruising/bleeding, swollen or painful abdomen due to enlarged spleen and liver, bone and joint pain and recurring infections.
How is B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) Diagnosed?
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) is diagnosed by complete blood count, peripheral blood smear, bone marrow aspiration and biopsy, cerebrospinal fluid examination for cases with CNS involvement, immunophenotyping and chromosomal analysis.
How is B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) Treated?
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) is treated with chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy and radiation therapy.
What is the Prognosis of B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL)?
The prognosis of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is generally good in children but is not as favorable in adults. Five year survival for patients with B-cell ALL is greater than 90% in children, but only 40% to 50% in adults and elderly patients, respectively.