Sézary syndrome is a leukemic variant of cutaneous T cell lymphoma defined by the presence of erythroderma, generalized lymphadenopathy and clonal T cells with cerebriform nuclei.
What is the Pathology of Sézary Syndrome?
The pathology of Sézary syndrome is:
-Etiology: The cause of Sézary syndrome is unknown.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Sézary syndrome involves the expression of the adhesion molecule cutaneous leukocyte antigen and the chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR10 which contribute to the homing of normal CD4+ T cells to the skin.
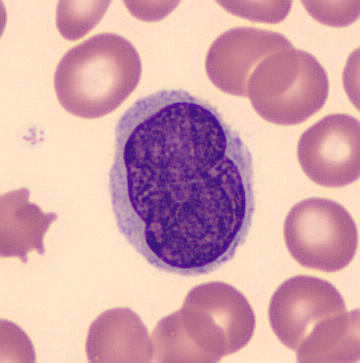
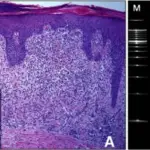
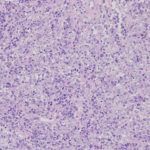
-Histology: The histology associated with Sézary syndrome is similar with mycosis fungoides. Sézary cells are seen as atypical lymphocytes of intermediate to large size and cerebriform nuclei. Lymph node shows complete effacement by monotonous infiltration of the Sézary cells.
How does Sézary Syndrome Present?
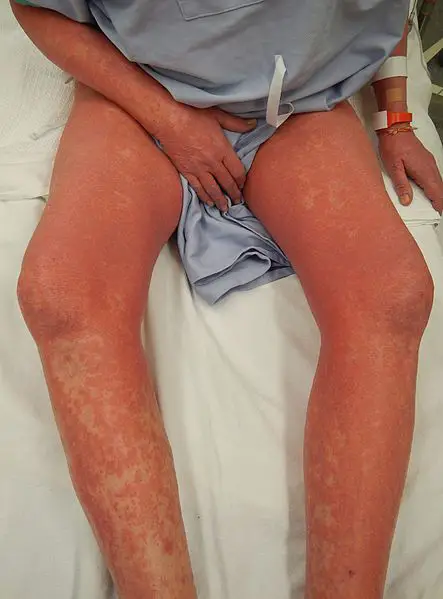
Patients with Sézary syndrome typically affects patients aged 60 to 70 with a male predilection of 2:1 ratio. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Sézary syndrome include erythroderma as its key feature for diagnosis defined as involvement of >80% of body surface and may range from mild to intense. Palms and soles usually show thickening, scales and fissures. Alopecia and plaques may occur. Nail dystrophy, blepharoconjunctivitis and ectropium can be present in late stages of the disease. Systemic symptoms are usually absent.
How is Sézary Syndrome Diagnosed?
Sézary syndrome is diagnosed based on clinical symptoms of erythroderma, generalized lymphadenopathy, clonal T cells and an absolute sezary cell count of ≥ 1 x 10^9/L on flow cytometry. An alternative diagnostic criteria on flow cytometry of ≥ 40% of CD4+ / CD7- and ≥ 30% of CD4+ / CD26- T cells may be helpful.
How is Sézary Syndrome Treated?
Sézary syndrome is treated with systemic therapies of retinoids, bexarotene, recombinant interferon a, conventional chemotherapy (CHOP) are used. Target therapies of Alemtuzumab, anti-PDA1,CD47/SIRPa may also be used. In patients with chronic conditions that are incurable, mainstay of treatment is control of symptoms and improvement of quality of life.
What is the Prognosis of Sézary Syndrome?
The prognosis of Sézary syndrome is poor with a median overall survival after diagnosis of 3.1-4 years. Median time to death after diagnosis is 3.5 years. 5 year overall survival range is 18-37%.