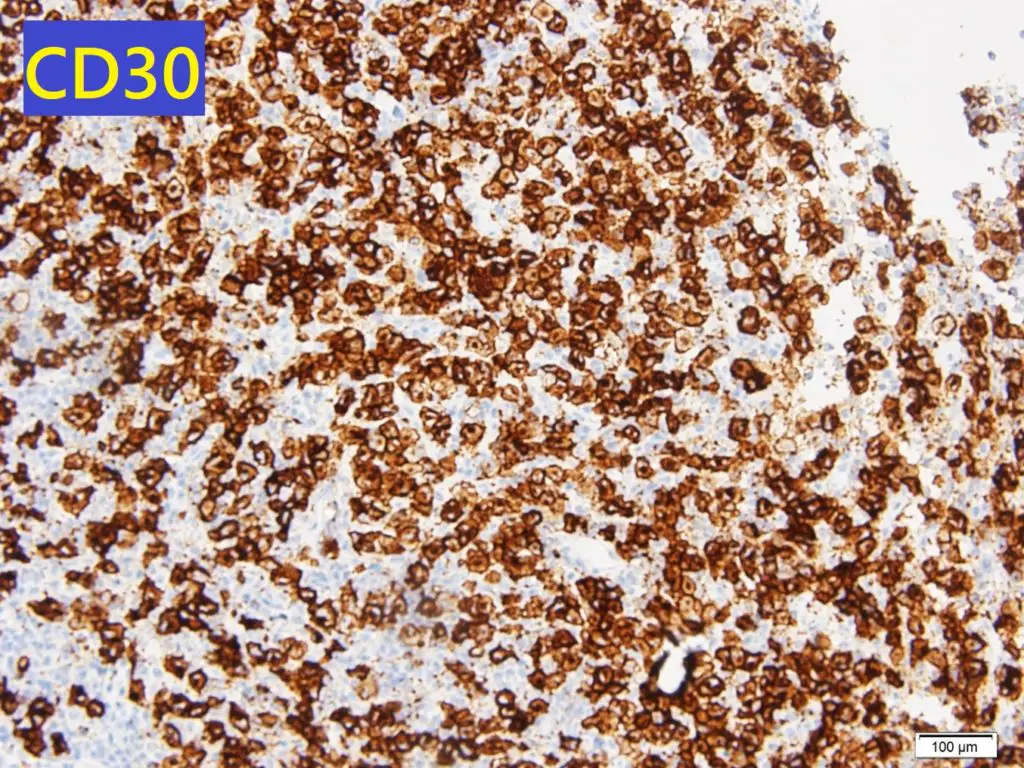
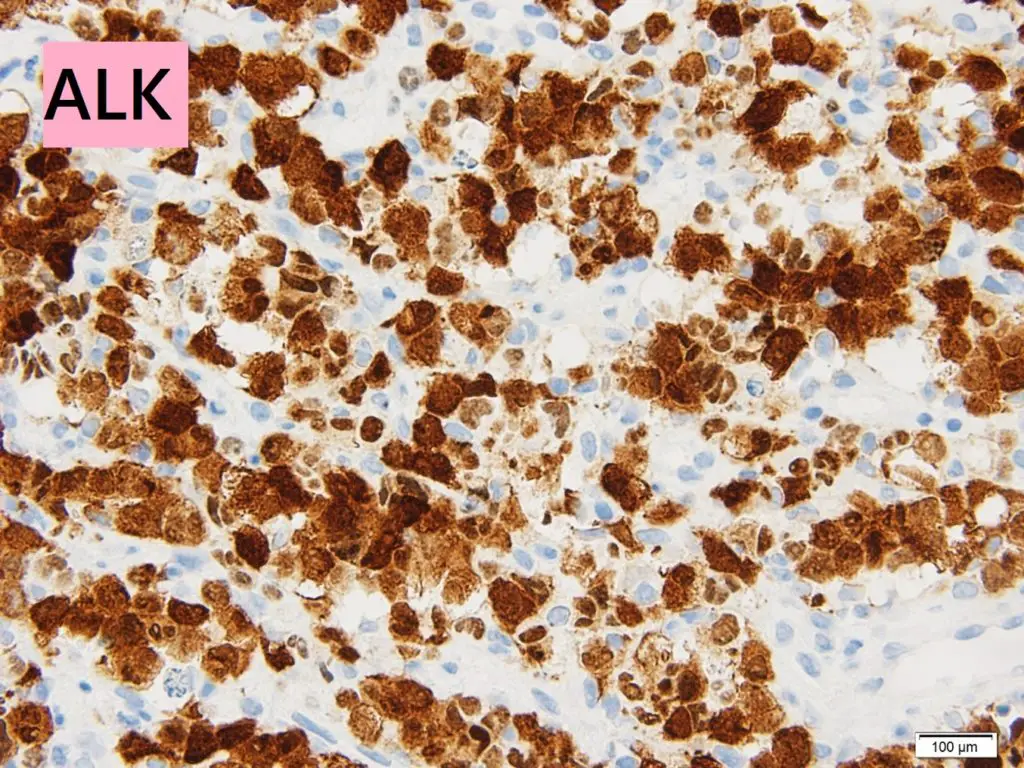
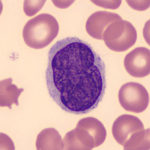
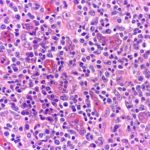
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is type of peripheral T cell lymphoma consisting of large lymphoid cells with abundant amphophillic cytoplasm, an ALK gene translocation and expression of ALK protein and CD30.
What is the Pathology of Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma?
The pathology of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is the presence of rearrangements in the ALK gene on chromosome 2p23.
-Genes involved: ALK gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to anaplastic large-cell lymphoma involve the rearrangements in the ALK gene on chromosome 2p23 which break the ALK locus and lead to the formation of chimeric genes encoding ALK fusion proteins constitutively active tyrosine kinases that trigger the RAS and JAK/STAT signaling pathways.
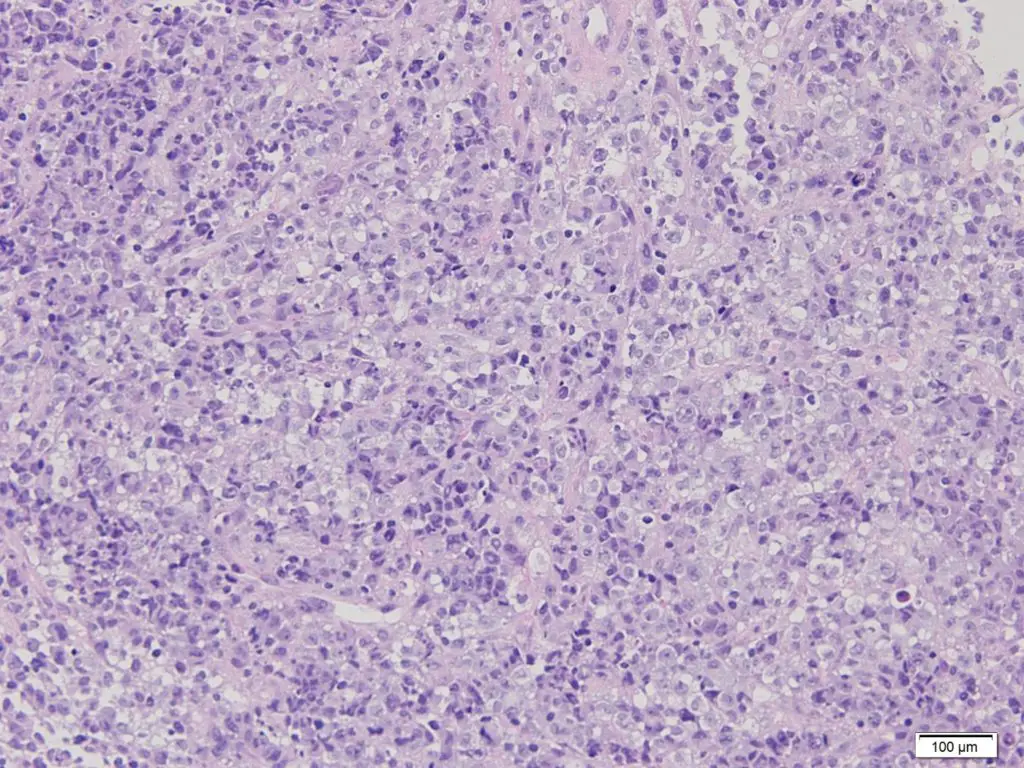
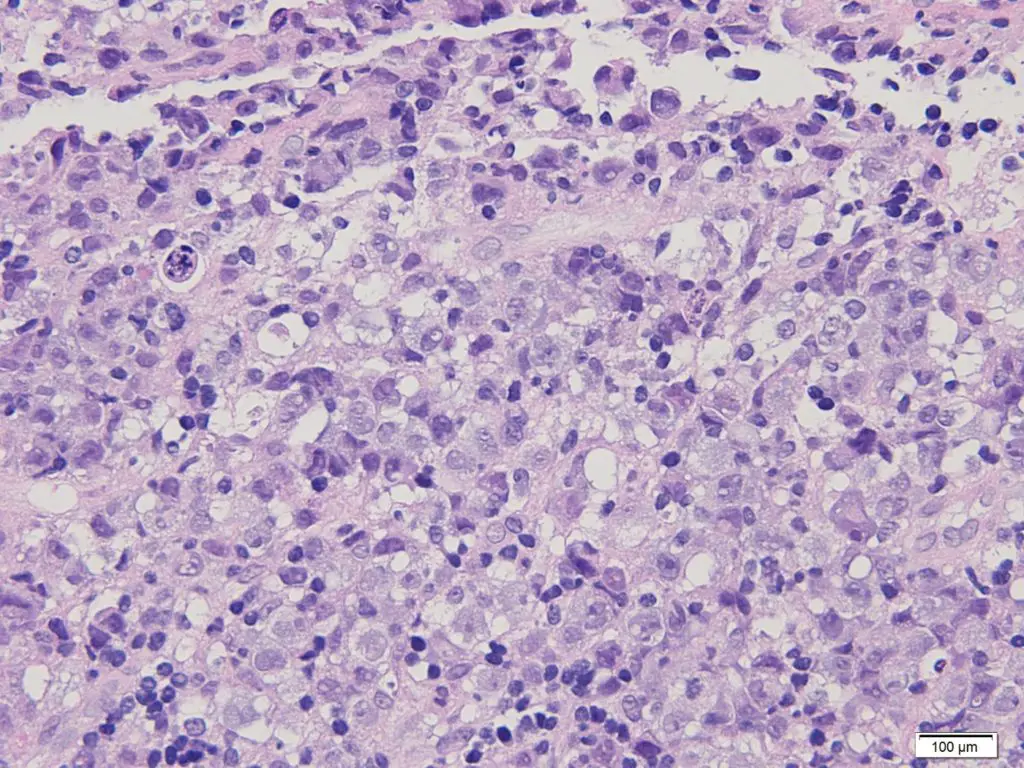
-Histology: The histology associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma shows large anaplastic cells, some containing horseshoe shaped nuclei and voluminous cytoplasm. The tumor cells cluster about venules and infiltrate lymphoid sinuses mimicking the appearance of metastatic carcinoma.
How does Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma Present?
Patients with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma typically affect children and young adults in the first 3 decades of life with a male predominance ratio of 1.5:1. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma include fever, weight loss, night sweats, peripheral or abdominal lymphadenopathy, extranodal infiltrates, bone marrow involvement, anemia and pancytopenia.
How is Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Anaplastic Large-cell Lymphoma is diagnosed by biopsy of the lymph node or the tissue and examining its morphology along with immunohistochemistry. Immunophenotype and detection of genetic abnormalities and T cell clone can be helpful.
How is Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma Treated?
Anaplastic Large-cell Lymphoma is treated with chemotherapy (CHOP treatment with or without Etoposide). Brentuximab vedotin and ALK inhibitors may be used for relapsed cases and for tumors that failed to respond to conventional chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma?
The prognosis of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is very good in children and young adults because this frequently involves soft tissues. The cure rate with chemotherapy is 75-80%. In adults with ALK negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma, the prognosis is worse.