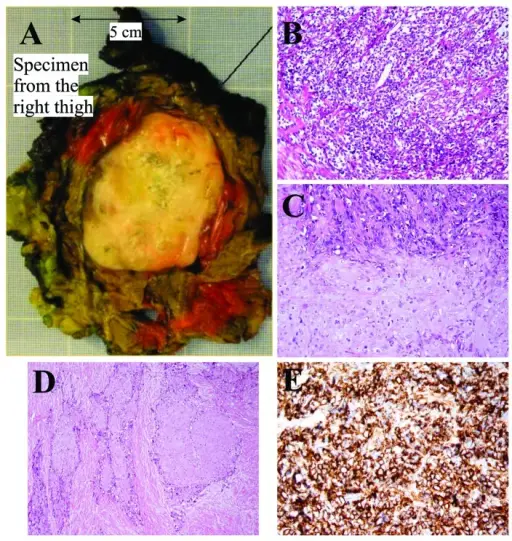
Neoplasia
Neoplasia means new growth.
Neoplasia begins as a single mutated cell.
Prior to the onset of the early clinical symptoms, there are about 30 cellular divisions of the neoplastic cell.
Neoplasia is not reparative.
Neoplasia is not hyperplasia.
Neoplasia is the unregulated, irreversible, and monoclonal development of new tissue.
For our purposes, neoplasia only contains a single monoclonal isoform.
Increased mutations result from each division.
Monoclonality
Monoclonal refers to the fact that the cancerous cells originate from a single abnormal “mother” cell.
Neoplasia (benign and malignant) are both monoclonal.
Benign tumors are monoclonal.
Malignant tumors are monoclonal.
The glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) enzyme isoforms can be used to help identify clonality.
Multiple isoforms of G6PD exist such as G6PDA, G6PDB, and G6PDC exist while only one isoform is inherited from each parent.
The X chromosome contains G6PD.
One isoform is randomly deactivated in each cell via lyonization (X-inactivation) in females.
In cells of any tissue, the normal ratio of active isoforms of G6PD is 1:1.
- 50% of cells contain G6PDA
- 50% of cells include G6PDB
Neoplastic monoclonal cells will express 100% of the same specific G6PD isoform.
Androgen receptor isoforms, which are also found on the X chromosome, can also be used to assess clonality.
B cell clonality is controlled by the immunoglobulin (Ig) light chain phenotype.
Chains both heavy and light make up Ig.
Either a kappa or lambda light chain is expressed by each B cell.
Ratio increases to greater than 6:1 or is inverted in hematopoetic malignancies.
Take these kappa to lambda ratios for example:
- k:l = 3:1 = normal
- k:l = 2:1 = normal
- k:l = 4:1 = normal
- k:l = 6:1 = abnormal
- k:l = 25:1 = abnormal
- k:l = 1:6 = abnormal
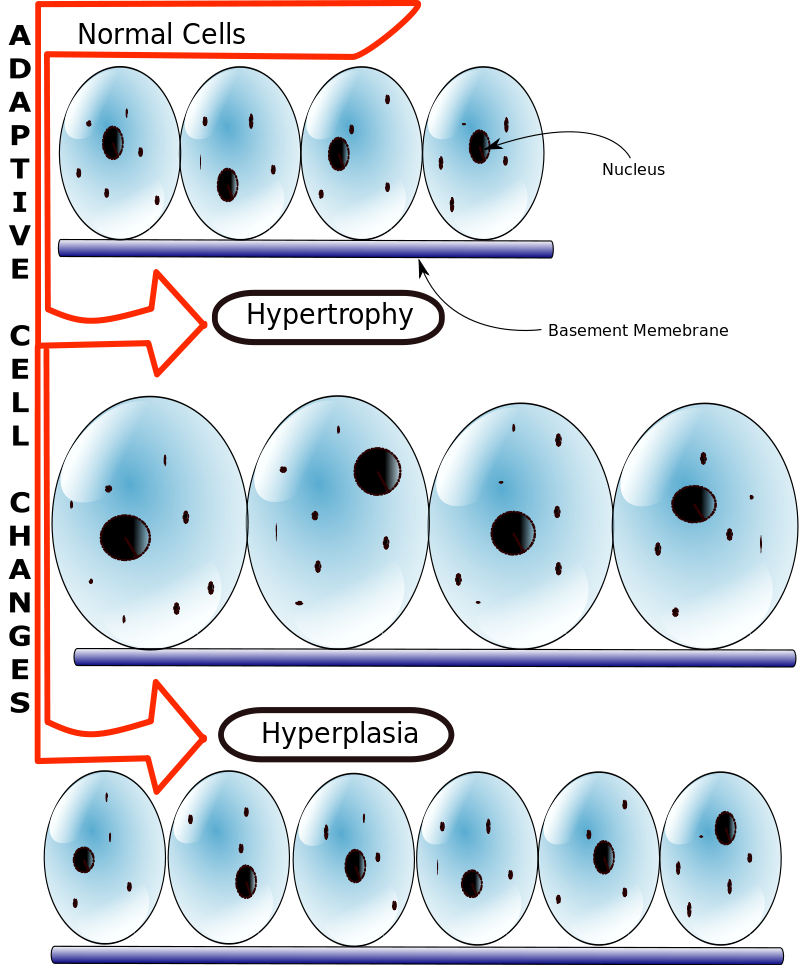
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia, which is polyclonal, meaning that cells are produced from many cells, maintains a 1:1 ratio.
In polyclonal hyperplasia, the ratio of kappa to lambda light chains is maintained.
Tumors
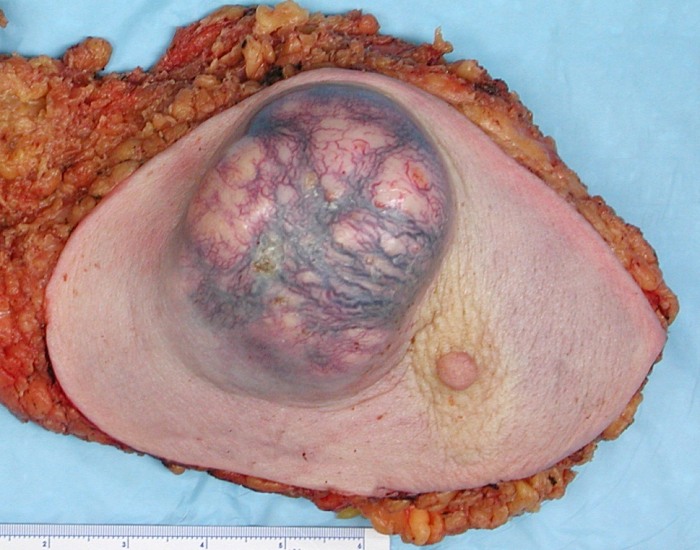
Both benign and malignant neoplastic tumors exist.
Benign tumors stay confined and do not spread.
Malignant tumors may infiltrate locally and spread (metastasize).
The classification of tumors is based on:
- Type of tissue produced
- Lineage of differentiation
- If the tumor is benign or malignant
Epidemiology of Neoplasia
The leading causes of death in adults are cardiovascular disease, followed by cancer, and cerebrovascular disease, respectively.
Accidental death in children is the most common cause of death, followed by cancer and congenital problems.
The information stated is making cancer the 2nd leading cause of death in both adults and children.
By incidence the three most prevalent cancers in the USA is:
- Breast cancer (in females) / prostate cancer (in males)
- Lung
- Colorectal cancers
The highest causes of adult cancer mortality in the USA is:
- Lung cancer
- Breast cancer (in females) / prostate cancer (in males)
- Colorectal cancer
Cancer Screening
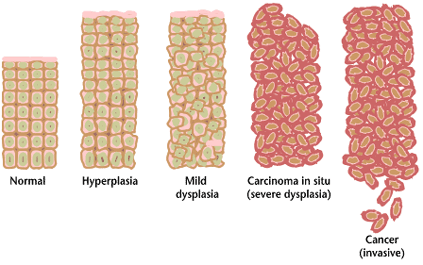
Early-stage cancers will have experienced more divisions and, consequently, more mutations than cancers that do not manifest symptoms until later in the disease.
The prognosis for cancers with late detection is usually poor.
The goals of cancer screening are:
- To catch dysplasia before it becomes carcinoma
- To detect carcinoma before clinical symptoms arise
Common screening methods include:
- Cervical pap smear
- Breast examination
- Breast ultrasound
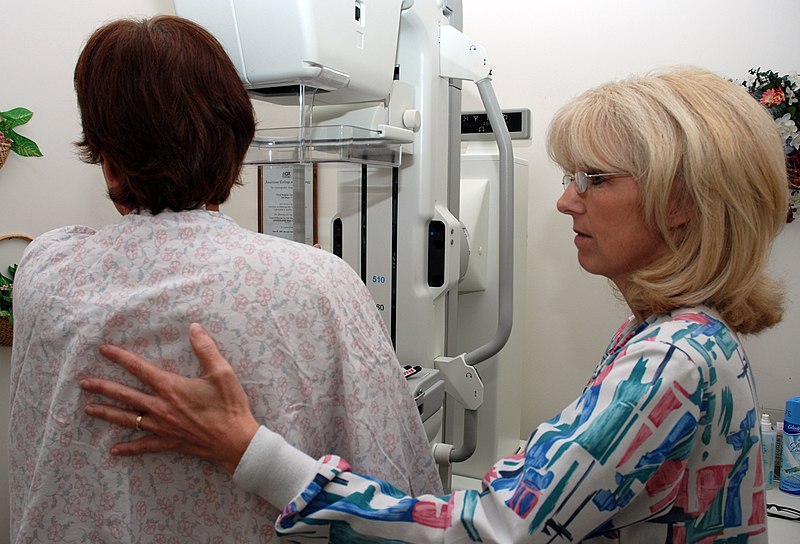
- Mammography
- Low dose computed tomography for adults 50-to-80-years-old with 20 years of smoking history
- Prostate exams aka digital rectal examination (DRE)
- Prostate specific antigen (PSA) level detection
- Endoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Hemoccult test
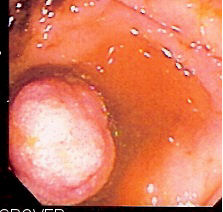
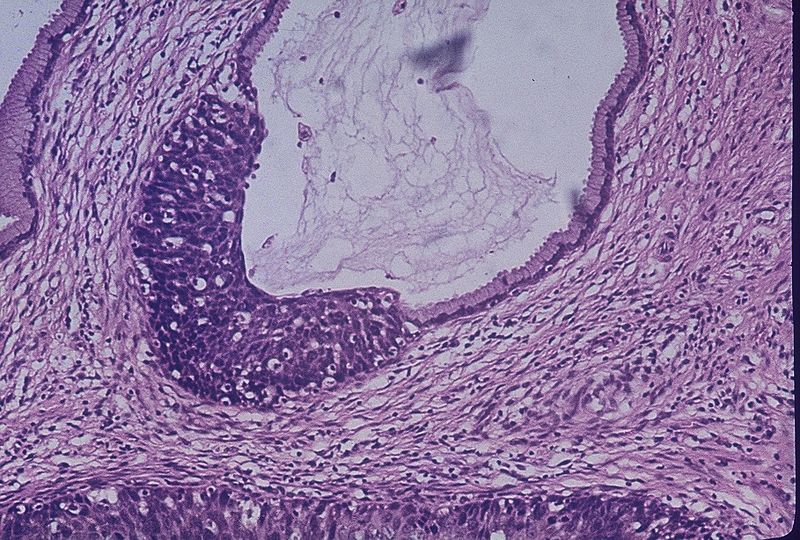
Cervical dysplasia (CIN), which can develop into cancer, is discovered by Pap smear.
Breast examination, breast ultrasound, and mammography may identify breast cancer.
Mammography can identify carcinoma in situ, such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), before it invades or invasive carcinoma, before it becomes clinically palpable.
Low dose CT can be used to detect lung cancer in at risk (smokers) individuals.
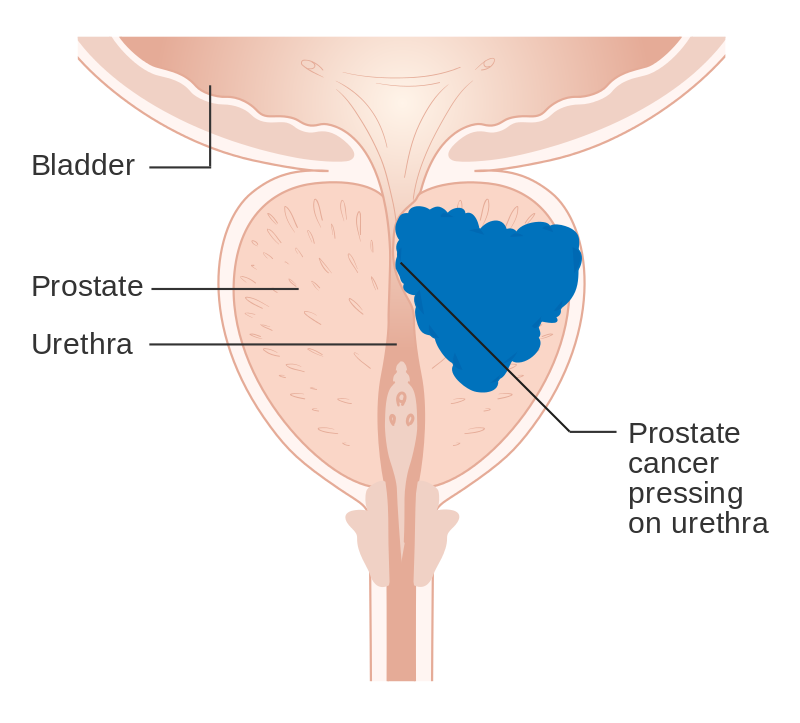
Prostate examination and PSA levels may help screen for prostate cancer.
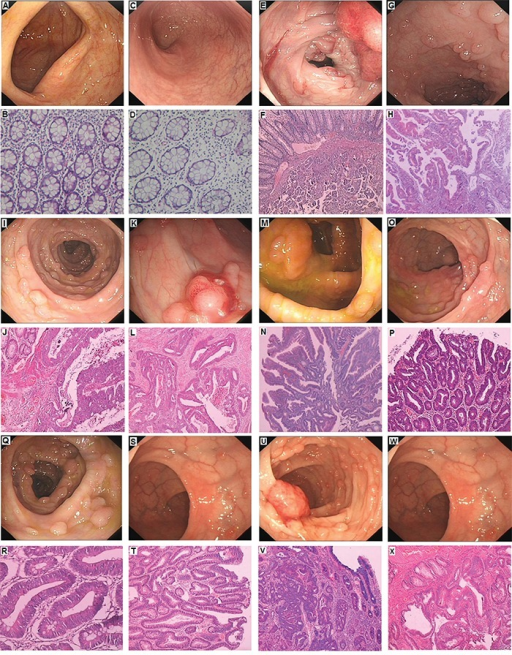
Endoscopy, colonoscopy, and the hemoccult test may be used to detect precancerous lesions in the gastrointestinal tract such as:
- Barrett’s esophagus
- Tubular adenomas
Carcinogenesis
Agents known as carcinogens cause DNA damage, which raises the risk of cancer.
Types of carcinogens include:
- Radiation (e.g. ionizing radiation)
- Oncogenic viruses (e.g. Epstein Barr virus)
- Chemicals (e.g. aflatoxins)
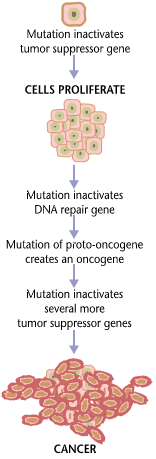
Damage to the DNA of the cells is what causes cancer to arise.
Although the damage is irreparable, it does not cause death.
DNA changes eventually cause major regulatory mechanisms to break down, which enables the promotion, growth, and spread of tumors.
Disrupted systems include proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and regulators of apoptosis.
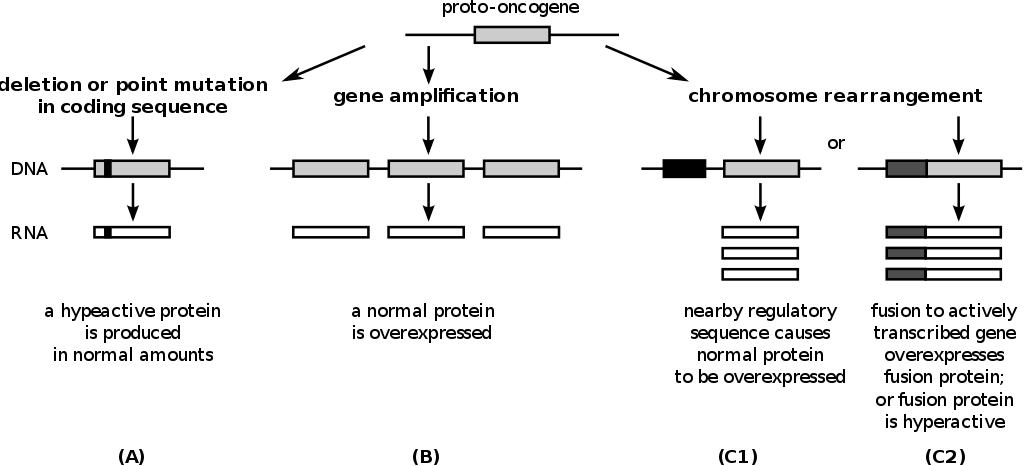
Oncogenes
Cell development and differentiation depend on proto-oncogenes (good/normal).
These oncogenes (bad) are created by these proto-oncogene mutations, which cause uncontrolled cellular growth.
Growth factors, growth factor receptors, signal transducers, nuclear regulators, and cell cycle regulators are all proto-oncogenes that can be mutated and turned into oncogenes.
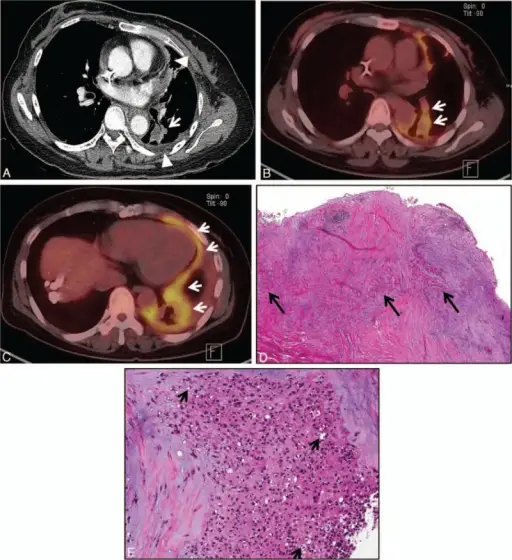
Growth factors, like PDGFB in an astrocytoma, stimulate cellular growth, whereas growth factor receptors operate as a conduit for the signals produced by growth factors.
ERBB2 (HER2/neu) in breast cancer, as an illustration.
Receptor activation is transmitted to the nucleus by signal transducers like Ras.
Ras is connected to growth factor receptors while the GDP is inactive.
GDP is changed into GTP by receptor binding, activating ras.
Ras that has been activated signals the nucleus to expand.
Ras deactivates by breaking down GTP into GDP.
GTPase activating protein enhances this.
However, mutant ras prevents GTPase activating protein from functioning.
Ras remains in its activated state longer as a result, producing more growth signals.
Cell cycle regulators, such cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase, mediate the cell cycle’s advancement.
Cell cycle regulators come together to form a complex that phosphorylates the proteins needed to move the cell through the cell cycle.
For example, the cyclinD/CDK4 complex phosphorylates the retinoblastoma protein, which promotes progression through the G/S checkpoint.
Tumor Suppressor Genes
As a result of controlling cell proliferation, tumor suppressor genes reduce or suppress the likelihood of developing tumors.
Classic examples of tumor suppressor genes are:
- p53
- Retinoblastoma
The development of the cell cycle from G1 to S phase is controlled by p53.
When DNA is damaged, it is also the p53 that slows the cell cycle and increases the activity of DNA repair enzymes.
When DNA repair is not an option, p53 triggers apoptosis and increases BAX, which interferes with Bcl-2.
Cytochrome c leaks from the mitochondria activating apoptosis.
Both copies of the p53 gene must be knocked out for tumor formation (Knudson two-hit hypothesis).
In more than 50% of malignancies, loss is visible.
Li-Fraumeni syndrome (2nd hit is somatic), caused by a germline mutation, is characterized by a propensity to develop various forms of sarcomas and carcinomas.
Additionally, Rb controls the transition from G1 to S phase.
The E2F transcription factor, which is required for moving into the S phase, is held by Rb.
E2F is released when the cyclinD/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) complex phosphorylates RB.
A Rb mutation causes constitutively free E2F, which permits cells to advance through the cell cycle and expand unchecked.
Both copies of Rb gene must be knocked out for tumor formation or Knudson two hit hypothesis.
Unilateral retinoblastoma is the characteristic manifestation of sporadic mutation, where both hits are somatic.
Familial retinoblastoma (second hit is somatic) is caused by a germline mutation and is characterized by bilateral retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma.
Apoptosis Regulation
They stop normal cells from apoptosis, but encourage it in mutant cells whose DNA cannot be repaired.
Normally, Bcl2 prevents the release of cytochrome c by stabilizing the mitochondrial membrane. While Cytochrome C can exit the mitochondria and start apoptosis when Bcl2 is disrupted.
Bcl2 is overexpressed in follicular lymphoma.
Further stabilization of the mitochondrial membrane prevents apoptosis.
Lymphoma is caused by the accumulation of B cells that would typically undergo apoptosis during somatic hypermutation in the lymph node germinal center.
Other Important Features of Tumor Development
Cell immortality requires telomerase which often becomes shorter with repeated cell divisions, which finally leads to cellular senescence.
Cancers often have upregulated telomerase, which preserves telomeres.
For a tumor to survive and grow, new blood vessels must be produced by angiogenesis.
Both the angiogenic factors FGF and VEGF are commonly generated by tumor cells.
Tumor survival requires avoiding immune surveillance.
The production of abnormal proteins, which are expressed in MHC class, is often the outcome of mutations.
By downregulating the expression of MHC class, CD8+ T cells can avoid immune surveillance and find and kill such altered cells as tumor cells.
Cancer risk is increased by primary and secondary immunodeficiency.
Tumor Invasion
Accumulation of mutations eventually results in tumor invasion and spread.
Typically, E-cadherin and other cellular adhesion molecules keep epithelial tumor cells attached to one another.
E-cadherin downregulation results in the separation of connected cells.
Basement membranes are destroyed by collagenase when cells connect to laminin.
Additionally, in the extracellular matrix, cells bind to fibronectin and localize via spreading.
Entrance into vascular or lymphatic spaces allows for metastasis.
Routes of Metastasis
Carcinomas are characterized by lymphatic spread.
Local draining lymph nodes first become affected by the spread.
Sarcomas and certain carcinomas, on the other hand, are characterized by hematogenous spread.
Hepatocellular carcinoma frequently invades the hepatic vein, while thyroid follicular carcinoma is another route.
Renal cell carcinoma frequently invades the renal vein.
The peritoneum is frequently involved in ovarian cancer, which is characterized by the seeding of bodily cavities.
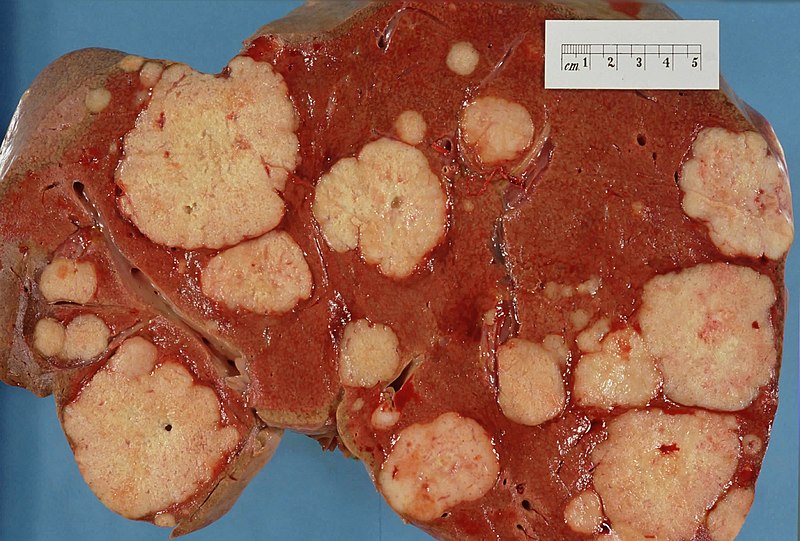
Clinical Features of Tumors
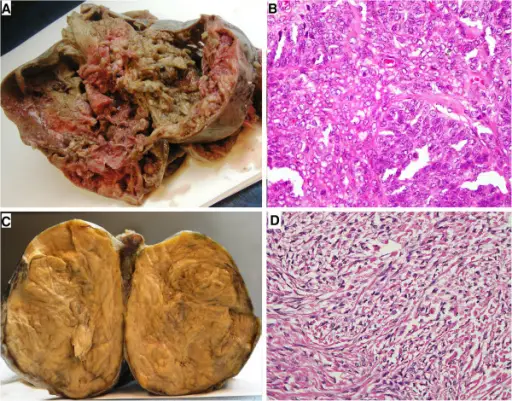
While malignant tumors are typically rapidly developing, poorly circumscribed, infiltrative, and fixed to nearby tissues and local structures, benign tumors are typically slow-growing, well-defined, distinct, and movable.
Before a tumor can be categorized as benign or malignant with absolute certainty, a biopsy or excision is required.
Some benign tumors can develop in a malignant-like manner, and vice versa for some malignant tumors.
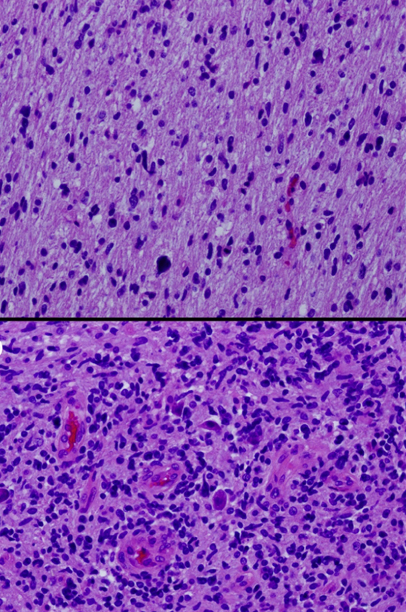
Histologic Features of Tumors
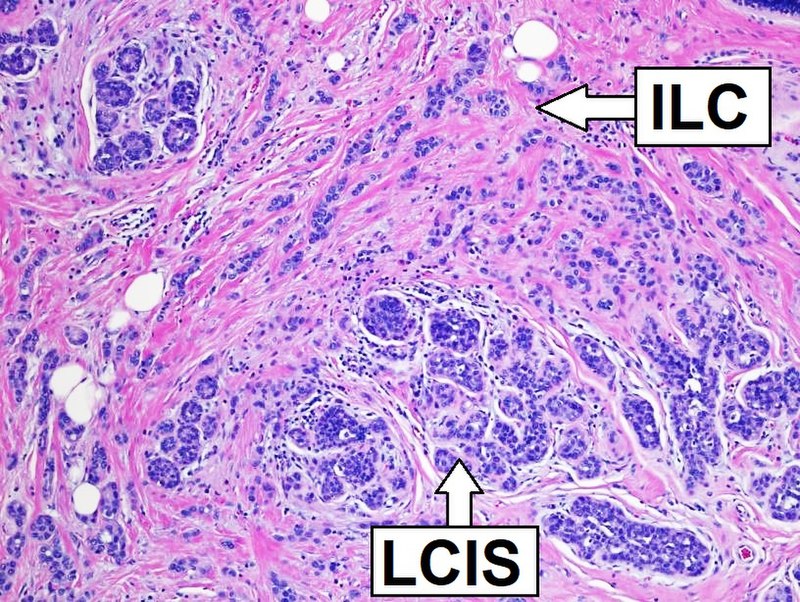
Tumors may be benign or malignant.
Benign tumors
Benign tumors are usually well differentiated.
Characteristics of benign tumors include:
- Organized growth
- Uniform nuclei
- Low nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
- Minimal mitotic activity
- Lack of invasion of basement membrane or local tissue
- Absence of metastatic potential
Malignant tumors
Benign tumors are usually poorly differentiated.
Characteristics of malignant tumors include:
- Disorganized development
- Nuclear pleomorphism
- Hyperchromasia
- High nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
- Increased mitotic activity
- Atypical mitosis
- Invasion through the basement membrane or into local tissue
Please note that the above lists represent general tumors.
Some benign tumors can look malignant.
Some malignant tumors can look benign.
Metastatic potential is the hallmark of malignancy.
Benign tumors cannot metastasize.
Malignant tumors can metastasize.
Tumors that are challenging to categorize on the basis of histology are characterized using immunohistochemistry.
Serum Tumor Markers
Proteins may be released by tumor into serum.
Serum tumor markers may be useful for screening, monitoring response to treatment, and monitoring tumor recurrence.
Elevated levels of serum tumor markers require tissue biopsy for diagnosis of carcinoma.
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) is a serum tumor marker used to screen for prostate cancer.
Cancer Grading
Grading is how bad the cancer looks.
A microscopic evaluation of differentiation that includes factors like how much a tumor resembles the tissue in which it develops.
Grading takes into account nuclear and architectural characteristics.
Low grade, well differentiated cells resemble normal parent tissue.
High grade, poorly differentiated cells do not resemble normal parent tissue.
The prognosis of a cancer depends on its grade since well-differentiated tumors have a better prognosis than those that do not.
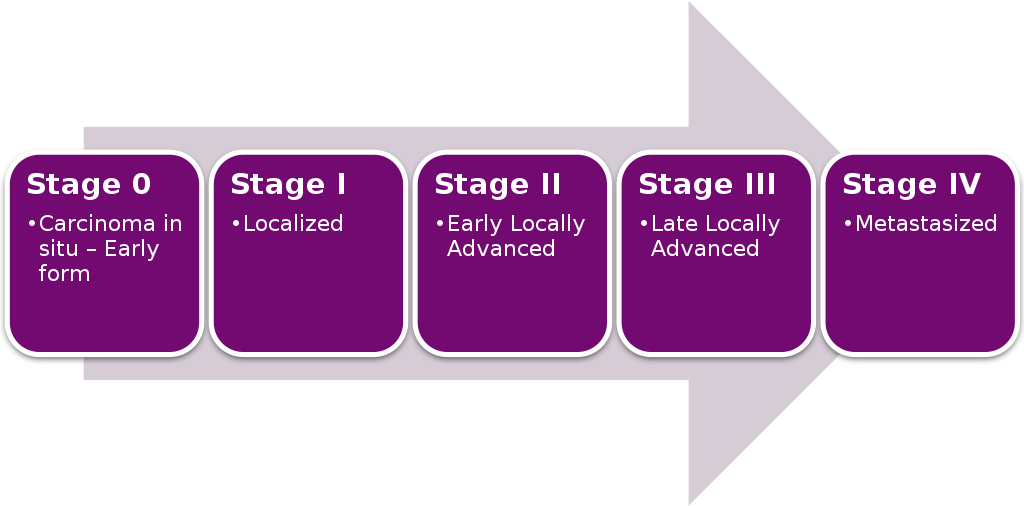
Cancer Staging
Staging is how far the cancer has gotten.
The staging of cancer is used to assess the size and spread of a cancer.
Cancer stage is a the most important prognostic factor.
Cancer stage is more important than cancer grade:
- Stage importance > grade importance
Cancer staging is determined following the final surgical removal of the tumor using the TNM staging system.
The acronym TNM stands for:
- T for tumor, or the size and/or depth of invasion
- N for nodes for regional lymph node spread, which is the second-most significant prognostic factor
- M for metastasis, which is the most significant prognostic component overall