Familial hypercholesterolima is a genetic defect in the LDL receptor that results in access accumulation of cholesterol.
What is Familial Hypercholesterolemia?
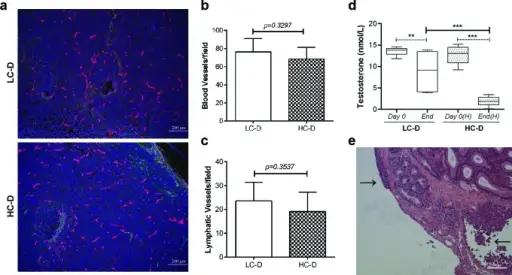
(a) Representative images show double immunofluorescence staining of tumor tissue sections using the panendothelial cell marker endomucin (red) and the lymphatic specific marker podoplanin (green). (b) Angiogenesis was not significantly different between hypercholesterolemic and control diet groups (p = 0.3297, n = 9 per group). (c) Immunostaining for lymphangiogenesis demonstrated no significant difference between the diet groups (p = 0.35, n = 9 per group). (d) Circulating testosterone level was measured at days 0 and 42 using a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence assay. Data were represented as mean ± SEM (**p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005). (e) Histopathology using H&E tissue sections demonstrated tumor cells invading into the capsule of the testes (arrows, tumors). Diet-induced hypercholesterolemia promotes androgen-independent prostate cancer metastasis via IQGAP1 and caveolin-1: Moon H, Ruelcke JE, Choi E, Sharpe LJ, Nassar ZD, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Parat MO, Shah A, Francois M, Inder KL, Brown AJ, Russell PJ, Parton RG, Hill MM - Oncotarget (2015). Not altered. CC.