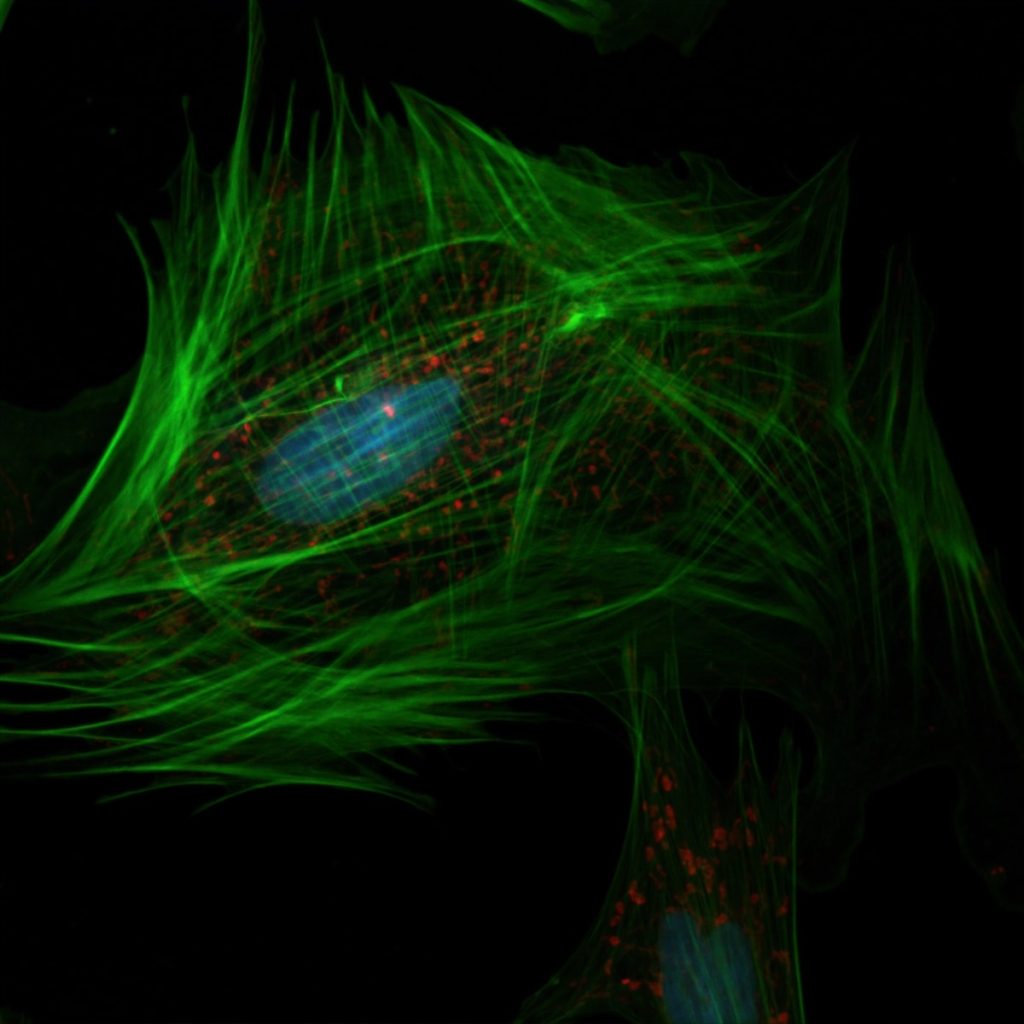
The cell is the smallest functional unit of life which live on its own and makes up all living organisms and tissues of the body.
What is the Genome?
The genome is an organism’s complete set of genetic instructions. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build that organism and allow it to grow and develop.
There are ~3 billion DNA base pairs and 20 thousand protein-encoding genes.
Non-protein coding genetic sequences include:
- Enhancer regions
- Promoter regions
- Binding sites
- Non-coding regulatory RNAs
- Mobile genetic elements
- Telomeres
- Centromeres
DNA variation is commonly due to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number variations (CNVs).
What are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms?
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur when a single nucleotide is replaced by another nucleotide in a certain stretch of DNA which may lead to variations in amino acid sequences.
What are Copy Number Variations?
Copy number variations (CNVs) arise when the number of copies of a particular gene varies from one individual to the next.
What is Epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the study of how cells control gene activity and changes in gene functions which are heritable but are not attributed to the changes in DNA sequences.
What are Histones?
Histones are the basic proteins associated with DNA which help the DNA to condense in chromatin. These are positively charged which attract the negatively charged DNA and help it to condense.
What are Histone Modifying Factors?
Histone modifying factors are post translational modifications of histone proteins which include:
- Histone acetylation
- Histone methylation
- Histone phosphorylation
What is Histone Acetylation?
Histone acetylation involves lysine residues incorporating within the N-terminal tail protruding from the histone core, which results in acetylation. Histone acetylation reduces the electrostatic affinity between histone proteins and DNA, and thus promotes a chromatin structure that is more permissive to gene transcription. Histone acetylation results in increased expression of the genes in the acetylated region.
What is Histone Methylation?
Histone methylation is when methyl groups are transferred to amino acids of histone proteins, it can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated. Histone methylation typically results in decreased expression of the genes in the methylated region.
What is Histone Phosphorylation?
Histone phosphorylation involves a phosphate group being attached to amino acids of histone, which confers negative charge to histones that results in more open chromatin conformation.
What are Nucleosomes?
Nucleosomes are sections of DNA wrapped around histone proteins.
What is DNA Methylation?
DNA methylation results in methyl groups being added to the DNA molecules at C5 position of cytosine to make it 5-methylcytosine. DNA methylation regulates gene expression by inhibiting the binding of transcription factors to DNA.
What are Chromatin Organizing Factors?
Chromatin organizing factors: histone chaperones, histone modifying enzymes and ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling complexes.
What is RNA?
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is single stranded molecule which has function to convert information stored in DNA to proteins.
What is MicroRNA?
MiroRNA (miRNA) is a small single-stranded non-coding RNA molecule about 22 nucleotides long which to control the amount of making of proteins in cell.
What is Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)?
Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) are transcripts more than 200 nucleotides long that is not translated into protein. Long noncoding RNA can modulate chromatin structure, function, and the transcription of neighboring and distant genes. Long noncoding RNA can also affect RNA splicing, stability and translation.
What is Cellular House Keeping?
Cellular house-keeping are activities which take place at specific sites in the cell that control local signaling such as protein signaling. Housekeeping genes are typically expressed because they are essential to a cell survival. These cellular house-keeping activities take place in membrane-bound intracellular organelles.
What is the Plasma Membrane?
The plasma membrane is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the external extracellular environment.
What is Passive Membrane Diffusion?
Passive membrane diffusion is a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes.
What is Carrier Mediated Membrane Transport?
Carrier mediated membrane transport is a cellular transport mechanism that is mediated by carriers. Carriers are membrane transport proteins which are involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, across the cell membrane.
What are Cellular Channels?
Cellular Channels are hydrophilic pores across membranes which are formed by channel proteins and mediate passive transport of solutes by forming an aqueous diffusion pore.
What is Receptor Mediated Uptake?
Receptor mediated uptake involves a specific receptor on the cell surface binds tightly to the extracellular macromolecule (the ligand) that it recognizes. The plasma-membrane region containing the receptor-ligand complex then undergoes endocytosis, becoming a transport vesicle.
What is Fluid-Phase Uptake?
Fluid-phase uptake is a process in which cells incorporate fluid from by a process designated as fluid-phase endocytosis.
What is Endocytosis?
Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle.
What is Exocytosis?
Exocytosis is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules out of the cell. It requires the use of energy to transport material.
What is Transcytosis?
Transcytosis is a type of transcellular transport in which various macromolecules are transported across the interior of a cell.
What is Caveolae-Mediated Endocytosis?
Caveolae-mediated endocytosis is a clathrin-independent endocytic process which involves bulb-shaped, 50-60 nm plasma membrane invaginations called caveolae.
What is Pinocytosis?
Pinocytosis is a process by which the cell takes in the fluids along with dissolved small molecules.
What is Receptor Mediated Endocytosis?
Receptor mediated endocytosis involves receptor proteins on the cell surface that are used to capture a specific target molecule by the inward budding of the plasma membrane.
What is The Cellular Cytoskeleton?
The cellular cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells.
Important filaments of the cytoskeleton include:
- Actin microfilaments
- Intermediate filaments
Note that examples of intermediate filaments include:
- Lamin A, B, and C
- Vimentin
- Desmin
- Neurofilaments
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)
- Cytokeratins
- Microtubules
Cells communicate and interact via junctions. Cellular junctions include:
- Occluding junctions
- Anchoring junctions (desmosomes)
- Communicating junctions (gap junctions)
Enzymes and structural proteins of the cell are continuously renewed. Cellular waste disposal is mediated via proteasomes and lysosomes.
What are Proteosomes?
Proteosomes are protein complexes that degrade unecesary or damaged proteins by proteolysis.
What are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles with roles in processes involved in degrading and recycling cellular waste, cellular signaling and energy metabolism.
What is Cellular Metabolism?
Cellular metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms in order to maintain life.
What are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles which generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell’s biochemical reactions.
What is Oxidative Phosphorylation?
Oxidative phosphorylation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy.
What is Cellular Energy Generation?
Cellular energy generation involves series of metabolic processes by which living cells produce energy through the oxidation of organic substances such as glucose.
What is ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things which captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food.
What is Intermediate Metabolism?
Intermediate metabolism involves molecules that are the precursors or metabolites of biologically significant molecules such as acetyl CoA.
What is Mitochondrial Function?
Mitochondrial function is a principal regulator of essential cell processes, acting as a control centre for cell behaviour and survival.
What is Cellular Activation?
Cellular activation is the ability to accelerate cellular functions which is done by differentiation of certain cells into more mature cells that exhibit different structural and functional form.
What is Cell Signaling?
Cell signaling is the fundamental process by which specific information is transferred from the cell surface to the cytosol and ultimately to the nucleus.
What are Signal Transduction Pathways?
Signal transduction pathways are pathways by which a cell responds to substances outside the cell through signalling molecules found on the surface of and inside the cell.
Examples of signal transduction pathways include:
- Kinase activity in signal transduction pathways involve controlling cell growth and proliferation to the initiation and regulation of immunological responses
- Tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell
- G-protein coupled receptors act like an inbox for messages in the form of light energy, peptides, lipids, sugars, and proteins
- Nuclear receptors are a family of ligand-regulated transcription factors that are activated by steroid hormones, such as estrogen
- Wnt protein ligands are secreted glycoproteins that are cysteine-rich and highly hydrophobic which bind to N-terminal extra-cellular cysteine-rich domain
- Notch family receptors are cell-surface receptors that transduce short-range signals by interacting with transmembrane ligands
What are Transcription Factors?
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to the upstream regulatory elements of genes in the promoter and enhancer regions of DNA and stimulate or inhibit transcription. The DNA binding domain is involved with transcription because it gives the ability to bind to specific sequences of DNA called enhancer or promoter sequences.
What are Growth Factors and Receptors?
Growth factors and receptors are transmembrane proteins which bind to specific growth factors and transmit the instructions conveyed by the factors to intracellular space. The main role of growth factors is to promote cell growth and division.
Types of growth factors include:
- Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
- Transforming growth factor α (TGF-α)
- Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)
- Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
- Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs)
- Fibroblast growth factors (FGF)
- Transforming growth factors (TGFs)
What are the Interactions with the Extracellular Matrix?
Interactions with the extracellular matrix include:
- Basement membrane foundation
- Mechanical support
- Scaffolding for tissue renewal
There are two basic forms of the extracellular matrix:
- Basement membrane
- Interstitial matrix
Components of the extracellular matrix include:
- Fibrous structural proteins like elastin and collagen
- Adhesive glycoproteins that aid with connectivity
- Water-hydrated gels like hyaluronic acid and proteoglycans
What are the Types of Collagen?
Types of collagens include:
- Type I
- Type II
- Type III
- Type IV
- Type V
What is Elastin?
Elastin is a key protein of the extracellular matrix which is highly elastic and present in connective tissue them to resume their shape after stretching or contracting.
How are Cell Populations Maintained?
Cell populations are maintained via the cell cycle which a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides.
What is the Cell Cycle?
The cell cycle involves four phases:
- G1 phase: The cell increases in size
- S phase: Copies its DNA
- G2 phase: Prepares to divide
- M phase: Mitosis
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are basic cells that can become almost any type of cell in the body under specific conditions.
Embryonic stem cells are derived from the undifferentiated inner mass cells of a human embryo they are pluripotent, meaning they are able to grow.
Tissue stem cells are undifferentiated cell, capable of proliferation, self-renewal, production of a large number of differentiated functional progeny, regenerating tissue after injury.