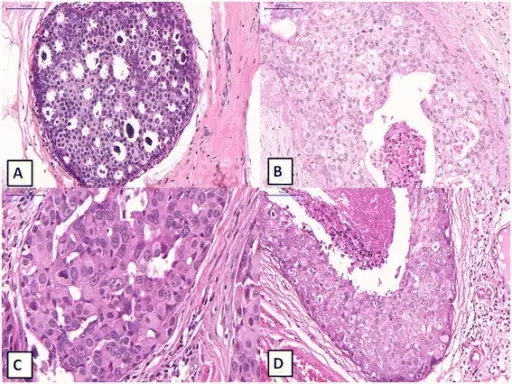
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a neoplastic proliferation of mammary ductal epithelial cells confined to the ductal-lobular system without evidence of invasion through the basement membrane into the surrounding stroma.
What is the Pathology of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ?
The pathology of ductal carcinoma in situ is:
-Etiology: The cause of ductal carcinoma in situ is not clear, but is thought to be due to genetic mutations occur in the DNA of breast duct cells.
-Genes involved: Mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ductal carcinoma in situ is the high estrogen states, such as use of oral contraceptive (OC) pills, nulliparity, advanced age at first birth, and also family history and genetic mutations.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with ductal carcinoma in situ may be a lump.
-Histology: The morphology associated with ductal carcinoma in situ shows cohesive sheets and aggregates. Microcalcifications may be present.
How does Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Present?
Patients with ductal carcinoma in situ typically are female present at age range of 50 – 59 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ductal carcinoma in situ include that majority are non-palpable and detected mammographically as microcalcifications.
How is Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Diagnosed?
Ductal carcinoma in situ is diagnosed by screening and diagnostic mammography, with final diagnosis confirmed by biopsy.
How is Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Treated?
Ductal carcinoma in situ is treated by breast conserving surgery alone or breast conserving surgery with radiotherapy or mastectomy and the adjuvant therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ?
The prognosis of ductal carcinoma in situ is good and patients diagnosed with DCIS have an excellent long-term breast-cancer-specific survival.