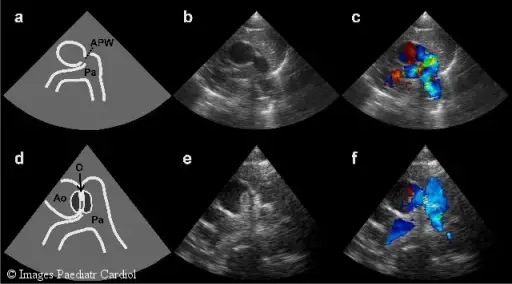
Two-dimensional echocardiography before and after intervention. (a) Schematic illustration and (b) two-dimensional high parasternal short-axis view demonstrating the defect and, (c) Doppler colour flow image with left-to-right shunt. (d) Schematic illustration and (e) two-dimensional high parasternal short-axis view showing the position of the occluder. (f) Doppler colour flow image without residual left-to-right shunt. The protrusion into the main pulmonary artery does not disturb the normal flow pattern. AO = aorta, APW = aortopulmonary window, PA = pulmonary artery, O = occluder.Transcatheter closure of symptomatic aortopulmonary window in an infant.
Pillekamp F, Hannes T, Koch D, Brockmeier K, Sreeram N - Images in paediatric cardiology (2008). Not Altered. CC.
Left-to-right shunts are characterized by back flow of blood from the systemic to pulmonary circulation.
Left-to-right shunts include:
- Atrial septal defect
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Ventricular septal defect
