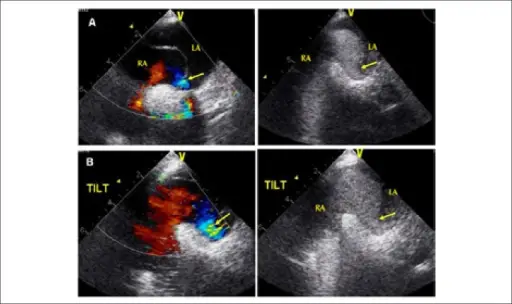
(A) Transesophageal echocardiogram in the dorsal decubitus position (0º) showingan exuberant atrial septal aneurysm with right-to-left shunt (arrow) evidenced oncolor Doppler and contrast medium flow; (B) Transesophageal echocardiogram on thetilt table (60°) with increased right-to-left flow evidenced on color Doppler andcontrast medium flow. Pseudo-pulmonary embolism--a case of hypoxemia associated with right-to-left shunt.
Faustino M, Soares AO, Rodrigues F, Anjos R, Freitas A, Gil VM - Arquivos brasileiros de cardiologia (2015). Not Altered. CC.
Right-to-left shunts are abnormal connections between the systemic and pulmonary vessels that cause deoxygenated blood to bypass pulmonary circulation and return to the body.
Examples of right-to-left shunts include:
- Tetralogy of fallot
- Transposition of the great arteries