Myocardial infarction is an irreversible heart muscle death caused by ischemia.
What is the Pathology of Myocardial Infarction?
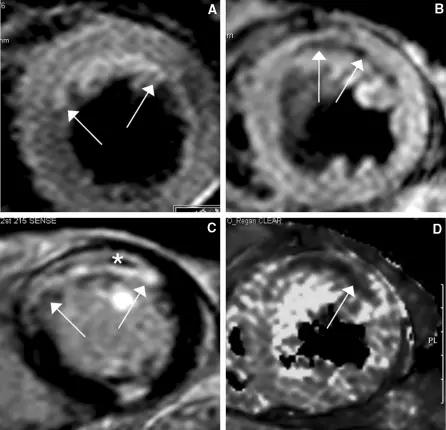
Myocardial infarction pathology is characterized by death of heart muscle (necrosis) due to blocked arteries.
How does Myocardial Infarction Present?
Myocardial infarction affects millions of Americans annually. Individuals typically present with chest pain that is preceded by fatigue, chest discomfort and malaise. Chest pain is prolonged and continuous for 30-60 minutes with radiation to neck, shoulder, jaws and left arm.
How is Myocardial Infarction Diagnosed?
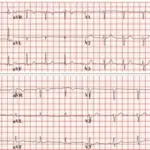
Myocardial infarction diagnosis include electrocardiogram, cardiac markers, CBC, metabolic panel, and lipid profile. Usual electrocardiogram findings are: ST-segment elevation, presence of new Q waves, ST-segment depression, T wave inversion. And nonspecific ST-T wave abnormalities.
How is Myocardial Infarction Treated?
Myocardial infarction treatment includes restoration of perfusion with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). Other pharmacologic management include: statins, aspirin, nitrates, and analgesia.
What is the Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction?
Myocardial infarction prognosis is poor with associated mortality of 30%; and 10% of survivors die after 1 year.