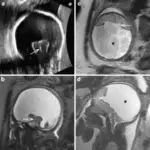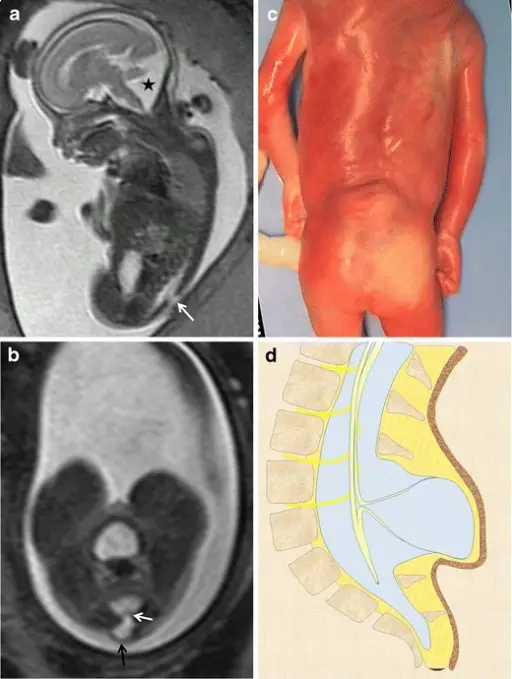
Myelocystocele. Fetus at 23 weeks’ gestation. a Sagittal T2-weighted HASTE image shows an interruption in the posterior vertebral arches in the lumbar region (arrow). A posterior fossa anomaly with an elevated vermis and dilation of the IV ventricle is also seen (asterisk). b Axial image at the lumbar level showing the cystic mass protruding through the spinal defect (black arrow). Two nerve roots (white arrow) can be seen arising from the non-neurulated neural placode inside the spinal defect. c Pathological specimen. d Sagittal diagram of the anomaly. Magnetic resonance imaging in the prenatal diagnosis of neural tube defects.
Zugazaga Cortazar A, Martín Martinez C, Duran Feliubadalo C, Bella Cueto MR, Serra L - Insights into imaging (2013). Not Altered. CC.
Posterior fossa anomalies congenital abnormalities that represent a wide variety of disorders of malformations and disruptions.
Examples of posterior fossa anomalies include:
- Chiari type I malformation
- Chiari type II malformation
- Arnold-Chiari malformation
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Joubert syndrome