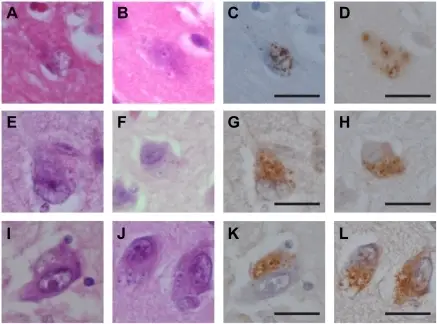
CHMP2B-positive granules correspond to GVDs.Cellular localization of CHMP2B (C, D, G, H, K, L) compared with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (A, B, E, F, I, J) in several neurodegenerative disorders is shown. CHMP2B-positive structures colocalized with the GVDs identified by HE staining and surrounded by a clear halo. A, C, Alzheimer's disease; B, D, myotonic dystrophy; E, G, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with dementia; F, H, Pick's disease; I, K, multiple system atrophy with parkinsonism; J, L, pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Scale bars represent 20 µm.Granulovacuolar degenerations appear in relation to hippocampal phosphorylated tau accumulation in various neurodegenerative disorders.
Yamazaki Y, Matsubara T, Takahashi T, Kurashige T, Dohi E, Hiji M, Nagano Y, Yamawaki T, Matsumoto M - PloS one (2011). Not Altered. CC.
Neurodegenerative diseases are degenerative nerve diseases that affect balance, movement, talking, breathing, and heart function. Many of these diseases are genetic. Most of them have no cure.
Examples of neurodegenerative diseases include:
- Alzheimer disease
- Frontotemporal degeneration
- Parkinson disease
- Atypical parkinsonism syndromes
- Multiple system atrophy
- Huntington disease
- Spinocerebellar degenerations
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Other motor neuron diseases