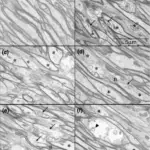
Neurofibromatosis. Microscopic aspect of neurofibroma with floret-like cells. A Overview to show diffuse infiltration of reticular dermis by neurofibroma, wherein cutaneous appendages (eccrine glands) appear permeated rather than dislocated by tumor cells. B Along the border to subcutaneous fat, neurofibroma cells tend to gradually merge with local adipocytes. C The cellular monotony of underlying neurofibroma is focally disrupted by large multinucleated cells (floret-like cells; arrows). These were felt to occur in a haphazard manner irrespective of local variation in tumor architecture. D High magnification view to show cytologic detail of two floret-like giant cells. Peripheral crowding of multiple nuclei along jagged cytoplasmic borders is appreciated in floret-like cell on center left. E Meissnerian-like differentiation is particularly frequent in – if not characteristic of – syndrome-associated neurofibromas. F An occasional tortuous peripheral nerve fascicle expanded by endoneurial tumor cells is felt to represent an elementary form of plexiform neurofibroma. All microphotographs represent slides stained by hematoxylin and eosin. Original magnifications: A – ×40; B, C, F – ×100; D – ×400; E – ×200.The riddle of multinucleated "floret-like" giant cells and their detection in an extensive gluteal neurofibroma: a case report.
Stanger K, De Kerviler S, Vajtai I, Constantinescu M - Journal of medical case reports (2013). Not Altered. CC.
Neurofibromatosis is a group of genetic disorders that cause tumors to form on nerve tissue.
What is the Pathology of Neurofibromatosis?
Etiology: The cause of Neurofibromatosis is a family history of the disorder.
Genes involved: NF1 and NF2.
Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to neurofibromatosis is caused by genetic defects.
Histology: The histology associated with neurofibromatosis shows proliferation of all elements of peripheral nerves. Schwann cells with wire-like collagen fibrils, mast cells, and stromal mucosubstance.
How does Neurofibromatosis Present?
Patients with neurofibromatosis typically are children of no more than 10 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with neurofibromatosis include cafe au lait spots, Lisch nodules, optic gliomas, and hearing issues.
How is Neurofibromatosis Diagnosed?
Neurofibromatosis is diagnosed by physical exam, and biopsy. Genetic tests for SMARCB1 and LZTR1 may be helpful.
How is Neurofibromatosis Treated?
Neurofibromatosis is treated by symptomatic management and prevention.
What is the Prognosis of Neurofibromatosis?
The prognosis of Neurofibromatosis is good.