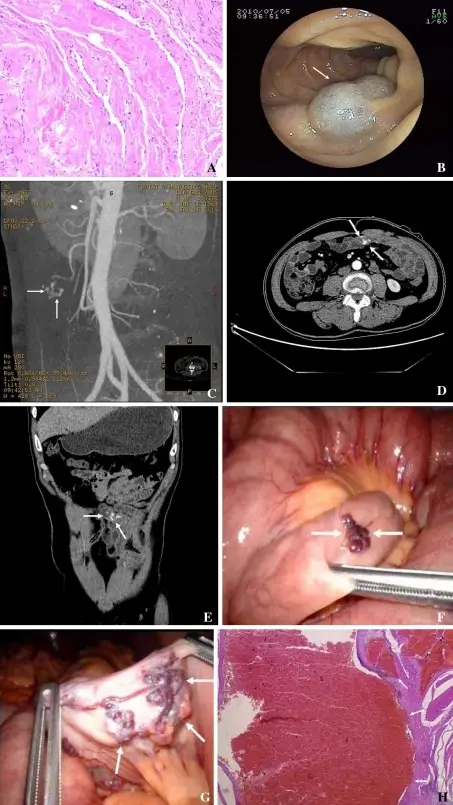
Skin, enteroscopy, abdominal contrast-enhanced CT, laparoscopic, and pathologic findings. A Histology shows cavernous angioma of the right knee (×400). B Angioma shown by enteroscopy examination through the mouth. C Arterio-venous malformation at a branch of the superior mesenteric artery shown by contrast-enhanced CT. D Contrast medium stays in the arterio-venous malformation on axial CT. E Contrast medium stays in the arterio-venous malformation shown by CT on coronal view reconstruction. F Small intestinal angioma (arrows) shown by laparoscopy corresponding to B. G Arterio-venous malformation (arrows) shown by laparoscopic approach, corresponding to C–E. H Histologic section of resected small intestinal arterio-venous malformation: vessel wall is irregular, distorted and dilated (×400). Small intestinal vascular malformation bleeding: diagnosis by double-balloon enteroscopy combined with abdominal contrast-enhanced CT examination.
Cui J, Huang LY, Wu CR - Abdominal imaging (2012). Not Altered. CC.
A malformation is a non-progressive, congenital morphologic anomaly of a single organ or body part due to an alteration of the primary developmental program.
Examples of malformations include:
- Cleft lip
- Cleft palate
- Congenital heart defect
- Neural tube defects
- Spina bifida