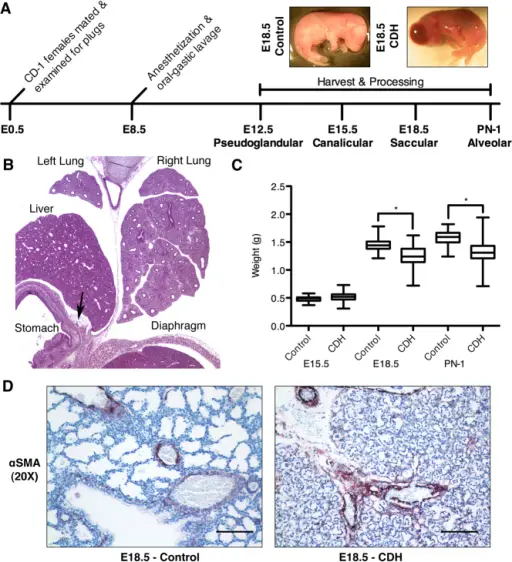
Model of teratogen-induced CDH. (A) Administration of nitrofen and bisdiamine yields a high rate of diaphragmatic defects in embryonic mice. Pregnant dams were anesthetized on day E8.5 of gestation and delivered a solution of 15 mg of nitrofen and 10 mg of bisdiamine in 400 μl of olive oil. Controls were administered olive oil alone. Administration of this solution resulted in the induction of hernia in 73% of embryos (data not shown). Representative images of E18.5 control and CDH embryos are shown. (B) Posterior view of a left-sided fetal CDH at gestational day E15.5 (H&E staining, 4× magnification). The diaphragmatic defect is highlighted with a black arrow. (C) The weight of embryos exposed to the nitrofen-bisdiamine solution. Significance is assumed at *P<0.05. (D) Immunohistochemistry of control and CDH (E18.5) sections with anti-aSMA confirm thickening of the pulmonary arteries characteristic of pulmonary hypertension. Images are displayed at 20× magnification. Scale bars: 100 μm.Timing and expression of the angiopoietin-1-Tie-2 pathway in murine lung development and congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
Grzenda A, Shannon J, Fisher J, Arkovitz MS - Disease models & mechanisms (2012). Not Altered. CC.
Teratogens are substances that may cause an abnormality following fetal exposure to the teratogen during pregnancy. The first half of pregnancy is the most vulnerable period to teratogens. The types or severity of abnormalities caused by a teratogenic agent depends on the genetic susceptibilities carried by the mother and the fetus.
Known teratogens include:
- Cyclopamine
- Lithium
- Thalidomide
- Valproic acid
- Vitamin A