Meniere’s disease is a feeling of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and sensation of ear fullness.
What is the Pathology of Meniere’s Disease?
The pathology of Meniere’s disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of Meniere’s disease is a distension of the membranous labyrinth by the endolymph.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Meniere’s disease is inner ear pressure abnormalities or abnormal cochlear neurons.
How does Meniere’s Disease Present?
Patients with Meniere’s disease are typically females in their 40s to 60s. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Meniere’s disease include tinnitus, intermittent episodic vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss, and ear fullness.
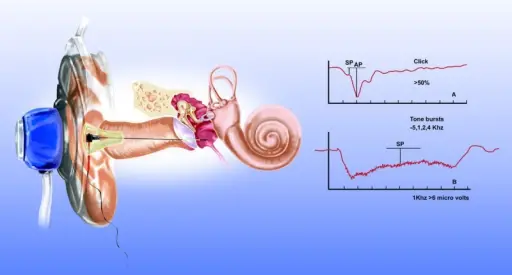
How is Meniere’s Disease Diagnosed?
Meniere’s disease is diagnosed by a hearing test, and specialized physical exam maneuvers.
How is Meniere’s Disease Treated?
Meniere’s disease is treated with diuretics, dietary modification, and vasodilators.
What is the Prognosis of Meniere’s Disease?
The prognosis of Meniere’s disease is fair. There is 70% improvement after therapy.