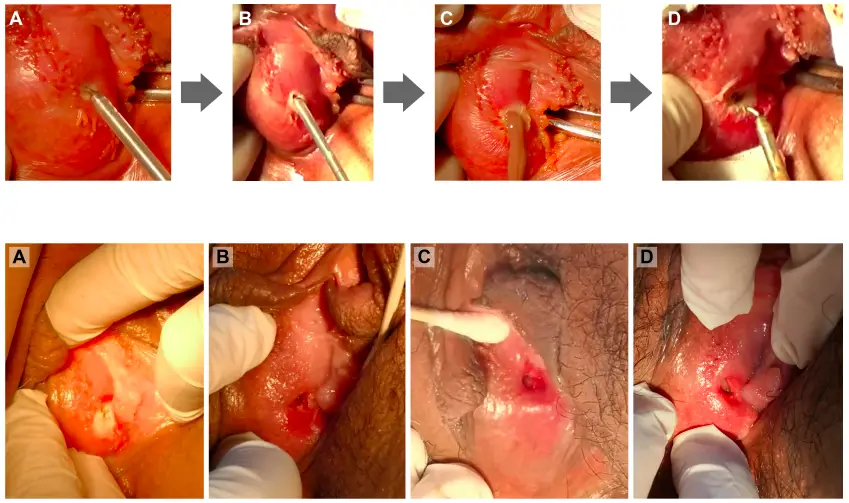
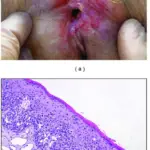
Bartholin cyst is the swelling at the opening of the Bartholin glands due to which openings of these glands become obstructed, causing fluid to back up into the gland.
What is the Pathology of Bartholin Cyst?
The pathology of Bartholin cyst is:
-Etiology: The cause of bartholin cyst is: infection, thick mucus, or swelling blocking the Bartholin gland duct.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to bartholin cyst involve ostium of the duct becomes blocked, leading to distention of the gland or duct with fluid causing cysts.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with bartholin cyst shows round bumps under the skin.
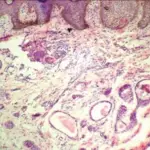
-Histology: The histology associated with bartholin cyst shows cysts lined by transitional or squamous epithelium or mucinous columnar epithelium.
How does Bartholin Cyst Present?
Patients with bartholin cyst typically females present at 20 to 30 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Bartholin cyst include tender or painful lump at vaginal opening, discomfort, or fever.
How is Bartholin Cyst Diagnosed?
Bartholin cyst is diagnosed by physical examination of the pelvis, and potential biopsy.
How is Bartholin Cyst Treated?
Bartholin cyst is treated by surgical drainage, Sitz baths, antibiotics, and possible marsupialization.
What is the Prognosis of Bartholin Cyst?
The prognosis of Bartholin cyst is good.