Acute endometritis is an inflammation or irritation of the lining of the uterus which is usually from an infection that passes through the cervix.
What is the Pathology of Acute Endometritis?
The pathology of acute endometritis is:
-Etiology: The cause of acute endometritis is infection due to chlamydia, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, more often after miscarriage or childbirth.
-Genes involved: NPSR1, ARID1A gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute endometritis is unknown.
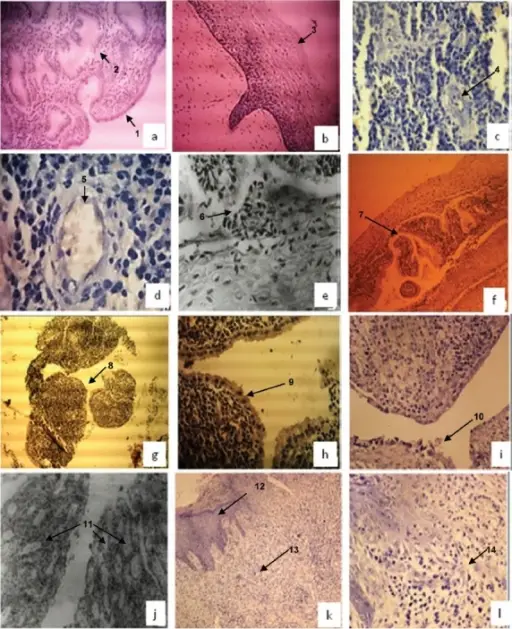
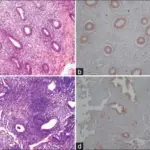
-Morphology: The morphology associated with acute endometritis shows abdominal symptoms.
-Histology: The histology associated with acute endometritis shows neutrophils infiltrating and destroying endometrial epithelium.
How does Acute Endometritis Present?
Patients with acute endometritis typically females who are close to menopause. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute endometritis include abnormal vaginal bleeding, swelling of the abdomen, bowel movement discomfort, and pelvic pain.
How is Acute Endometritis Diagnosed?
Acute endometritis is diagnosed by endometrial biopsy, bacterial cultures tests, laparoscopic procedures, blood tests for WBCs and RBCs.
How is Acute Endometritis Treated?
Acute endometritis is treated by antibiotics.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Endometritis?
The prognosis of acute endometritis is good. Endometritis usually goes away with antibiotics without any further problems. However, problems with reproduction and severe infections can occur if the condition isn’t treated. These can lead to infertility.