Adenomatoid tumors aka mesotheliomas are benign or malignant neoplasm of mesothelial origin involving the fallopian tubes.
What is the Pathology of Adenomatoid Tumors?
The pathology of adenomatoid tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of adenomatoid tumors is somatic missense mutations.
-Genes involved: TRAF7 mutation.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to adenomatoid tumors.
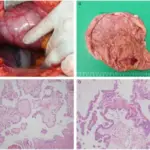
-Morphology: The morphology associated with adenomatoid tumors shows small, well-circumscribed, solitary masses that are tan-yellow, and solid mass.
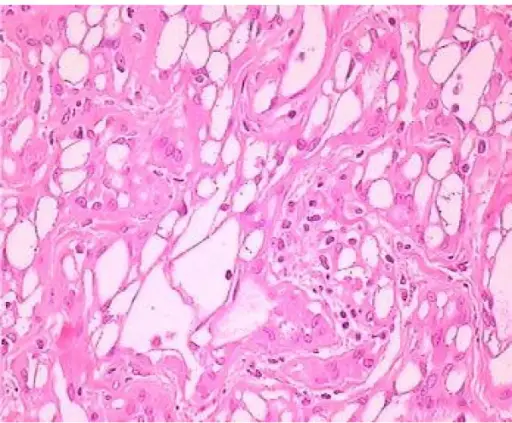
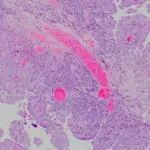
-Histology: The histology associated with adenomatoid tumors shows tubular spaces of varying size, eosinophilic cytoplasm, lymphocytic follicles.
How does Adenomatoid Tumors Present?
Patients with adenomatoid tumors typically females between 26 to 55 years age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with adenomatoid tumors include: abnormal vaginal bleeding, polymenorrhea, and menorrhagia.
How is Adenomatoid Tumors Diagnosed?
Adenomatoid tumors is diagnosed by: physical examination, trans-abdominal and trans-vaginal ultrasound, CT scan.
How is Adenomatoid Tumors Treated?
Adenomatoid tumors is treated by hysterectomy and bilateral salpingectomy, and surgical removal.
What is the Prognosis of Adenomatoid Tumors?
The prognosis of adenomatoid tumors is good. The surgical excision of benign tumors has no cases of recurrence reported till date.