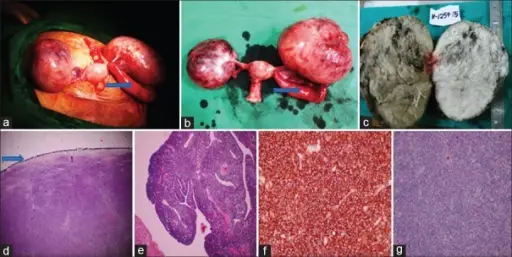
(a) Intraoperative finding showing enlarged bilateral ovaries, arrow pointing to enlarged left fallopian tube, (b) total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy specimen, arrow pointing to enlarged left fallopian tube, (c) cut section showing predominantly solid, homogenous, gray-white ovary with few small cysts and areas of hemorrhage, (d) on low power microscopy, ovary shows diffuse dense infiltrate of monomorphic neoplastic lymphoid cells with intact capsule (arrow), (e) low power microscopy of the left fallopian tube showing diffuse dense infiltrate of monomorphic neoplastic lymphoid cells consisting of medium-sized cells with round to oval nuclei, finely dispersed chromatin, and single to multiple small nucleoli, (f) immunohistochemistry showing tumor cells were diffusely and strongly positive for Tdt, (g) immunohistochemistry showing tumor cells were negative for B-cell marker CD-20. Primary T-cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma of the Ovary: A Case Report. Paediatric Oncology. Not Altered. CC.
Fallopian tube cysts are fluid-filled sacs which are benign and very small, but they can grow larger, can become >15 cm.
Examples of fallopian tube cysts include:
- Paratubal cysts
- Hydatids of morgagni
