Malignant mixed mullerian tumors are also called a carcinosarcoma, is a cancer which contains two types of cancer cells i.e., carcinoma and sarcoma cells. These tumors usually develop in tissues of the female genital tract.
What is the Pathology of Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumors?
The pathology of malignant mixed mullerian tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of malignant mixed mullerian tumors is unclear but accumulation of genetic mutations could be a factor.
-Genes involved: BRCA2 gene mutation.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to malignant mixed mullerian tumors are unknown however, it appears to have epithelial origin.
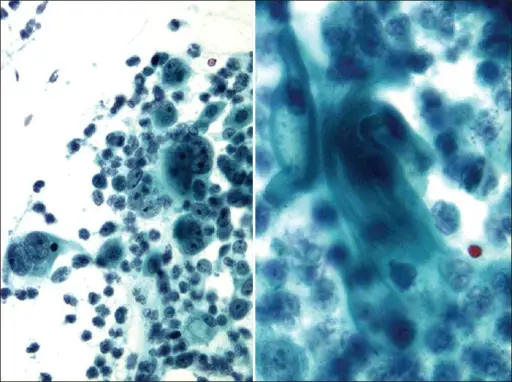
-Morphology: The morphology associated with malignant mixed mullerian tumors shows Soft and fleshy mass, often with bleeding and necrosis.
-Histology: The histology associated with malignant mixed mullerian tumors shows epithelial and sarcomatous elements which could be homologous or heterologous, rarely trophoblastic tissues.
How does Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumors Present?
Patients with malignant mixed mullerian tumors typically females mostly postmenopausal specially at their 60s. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with malignant mixed mullerian tumors include: vaginal bleeding, abnormal vaginal cytology and polypoidal cervical mass.
How is Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumors Diagnosed?
Malignant mixed mullerian tumors is diagnosed by: pelvic ultrasound, CT scan.
How is Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumors Treated?
Malignant mixed mullerian tumors is treated by surgical cytoreduction with adjuvant chemotherapy, radiation therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Malignant Mixed Mullerian Tumors?
The prognosis of malignant mixed mullerian tumors is poor. The 5 years survival rate is only 12-20%.