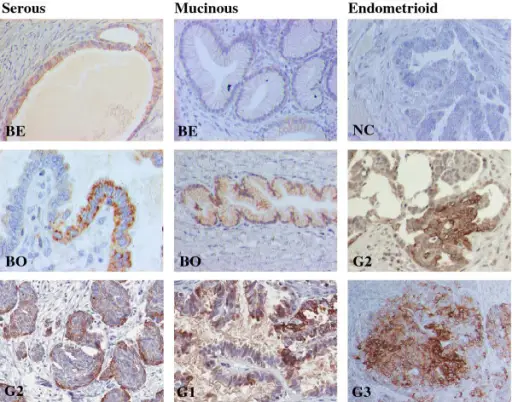
Endometrioid ovarian tumors is ovarian carcinoma resembling endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the endometrium.
What is the Pathology of Endometrioid Ovarian Tumors?
The pathology of endometrioid ovarian tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of endometrioid ovarian tumors is unknown.
-Genes involved: PTEN, CTNNB1, PIK3CA, KMT2D, KMT2B, PIK3R1, ARID1A and TP53.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to endometrioid ovarian tumors are: the molecular alterations cause changings in pathways especially beta catenin signaling pathway or PI3K pathway due to which the cell cycle s disturbed hence causing tumors.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with endometrioid ovarian tumors shows Cystic with solid component and areas of hemorrhage.
-Histology: The histology associated with endometrioid ovarian tumors shows Stromal invasion.
How does Endometrioid Ovarian Tumors Present?
Patients with endometrioid ovarian tumors typically are females with mean age of 50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with endometrioid ovarian tumors include abdominal distention and pain, pelvic pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, palpable mass, vaginal bleeding, dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia.
How is Endometrioid Ovarian Tumors Diagnosed?
Endometrioid ovarian tumors is diagnosed by blood tests for CA125, MRI, histological examinations.
How is Endometrioid Ovarian Tumors Treated?
Endometrioid ovarian tumors is treated by: surgery, chemotherapy for stage 1 and 2, platinum based therapy for advanced stages.
What is the Prognosis of Endometrioid Ovarian Tumors?
The prognosis of endometrioid ovarian tumors is good but depends on stages. 95% for stage 1 and 2 and 51% for stage 3 and 4.