Serous Tumors of the Ovary is the tumor arose from the serous membrane, in the epithelial layer in the abdominopelvic cavity.
What is the Pathology of Serous Ovarian Tumors?
The pathology of serous ovarian tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of serous ovarian tumors is nulliparity.
-Genes involved: BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to serous ovarian tumors normal fimbrial epithelium implanted on the denuded ovarian surface at the site of rupture when ovulation occurs, this tubal epithelium can result in the formation of a cortical inclusion cyst that can then undergo malignant transformation, hence resulting in disease.
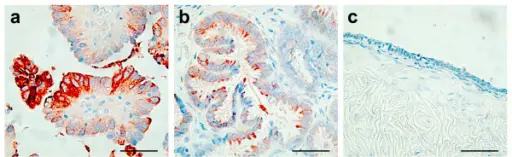
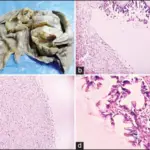
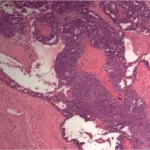
-Morphology: The morphology associated with serous ovarian tumors shows cystic, papillary, and solid growth.
-Histology: The histology associated with serous ovarian tumors shows malignant cells.
How does Serous Ovarian Tumors Present?
Patients with serous ovarian tumors typically females mostly at the age 45 to 60 years, The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with serous ovarian tumors include: pain, bloating, nausea, constipation, anorexia, difficulty eating and bowel and urinary changes.
How is Serous Ovarian Tumors Diagnosed?
Serous ovarian tumors is diagnosed by transvaginal ultrasonography, serum CA125 levels, biopsy, and genetic tests for BRCA mutations.
How is Serous Ovarian Tumors Treated?
Serous ovarian tumors is treated by: surgical cytoreduction for resection of tumors, adjuvant chemotherapy, platinum-taxane based chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Serous Ovarian Tumors?
The prognosis of serous ovarian tumors is good if detected at early stages. Those patients who are diagnosed with advanced-stage disease will develop treatment resistance, which inevitably heralds eventual mortality.