Sertoli-leydig cell tumors are a rare cancer of the ovaries which produce and release a male sex hormone called testosterone.
What is the Pathology of Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors?
The pathology of sertoli-leydig cell tumors is:
-Etiology: The cause of sertoli-leydig cell tumors is unknown but genetic mutations might be the cause.
-Genes involved: DICER1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sertoli-leydig cell tumors are germline mutations in DICER1, a gene encoding the RNase III enzyme in the microRNA maturation pathway.
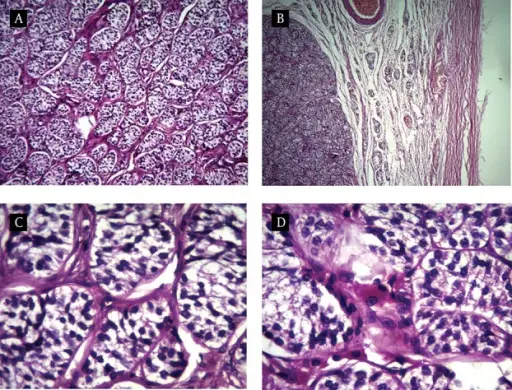
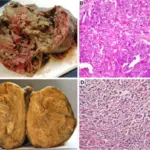
-Morphology: The morphology associated with sertoli-leydig cell tumors shows unilateral, solid cut surface, with cystic components.
-Histology: The histology associated with sertoli-leydig cell tumors shows Cystic component, Open or compressed Sertoli cell tubules, admixed with clusters of Leydig cells in the intervening stroma.
How does Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors Present?
Patients with sertoli-leydig cell tumors typically in females with a mean age of 25 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sertoli-leydig cell tumors include pelvic pain or a pelvic mass, hirsutism, clitoromegaly, breast atrophy and menstrual irregularity or amenorrhea.
How is Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors Diagnosed?
Sertoli-leydig cell tumors is diagnosed by: blood tests for testosterone levels, CT scan, MRI, ultrasound.
How is Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors Treated?
Sertoli-leydig cell tumors is treated by conservative fertility sparing surgery, lymphadenectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, platinum based adjuvant chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors?
The prognosis of sertoli-leydig cell tumors is good overall. Patients with germline DICER1 mutations have a favorable prognosis compared with those with somatic DICER1 mutations only.