Cholelithiasis is caused by excessive amounts of cholesterol in the bile that’s stored in the gallbladder and this cholesterol hardens to form stone-like substances.
Examples of cholelithiasis are:
- Gallstones
- Cholesterol stones
- Pigment stones
What are Gallstones?
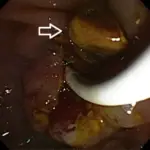
Gallstones are concretions that form in the biliary tract, usually in the gallbladder.
What is the Pathology of Gallstones?
The pathology of gallstones is:
-Etiology: The cause of gallstones isn’t completely understood.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gallstones is that the bile contains too much cholesterol or too much bilirubin.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with gallstones shows a cholesterol stone that results from the presence of too much cholesterol in the bile.
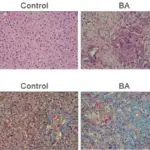
-Histology: The histology associated with gallstones shows diverse histopathological changes in gallbladder mucosa, namely acute inflammation, chronic inflammation, granulomatous inflammation, hyperplasia, cholesterolosis, dysplasia, and carcinoma.
How does Gallstones Present?
Patients with gallstones typically are female present at the age range of 30-50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gallstones include irritation and inflammation of the gallbladder.
How are Gallstones Diagnosed?
Gallstones are diagnosed via several different imaging techniques.
How are Gallstones Treated?
Gallstones are treated with laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Gallstones?
The prognosis of gallstones is good.