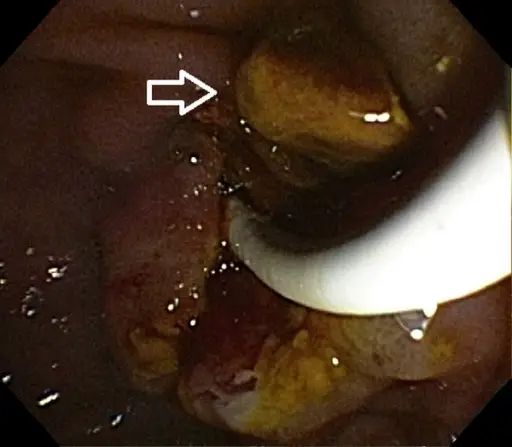
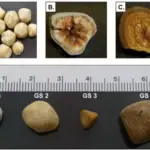
Cholesterol stones are formed when the bile is supersaturated with cholesterol, which may result from decreased bile acid production, increased cholesterol output in bile, or both.
What is the Pathology of Cholesterol Stones?
The pathology of cholesterol stones is:
-Etiology: The cause of cholesterol stones is often associated with inflammation.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cholesterol stones is that they’re formed when the bile is supersaturated with cholesterol.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with cholesterol stones shows that they’re usually yellow-green and are made of mostly hardened cholesterol.
-Histology: The histology associated with cholesterol stones shows that they contain more than 40% cholesterol.
How do Cholesterol Stones Present?
Patients with cholesterol stones typically are female present at the age range of adult age groups. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cholesterol stones include abdominal pain.
How are Cholesterol Stones Diagnosed?
Cholesterol stones are diagnosed with abdominal ultrasound.
How are Cholesterol Stones Treated?
Cholesterol stones may be treated with medications, such as ursodiol which works to break up small cholesterol stones. Cholecystectomy may also be useful.
What is the Prognosis of Cholesterol Stones?
The prognosis of cholesterol stones is good.