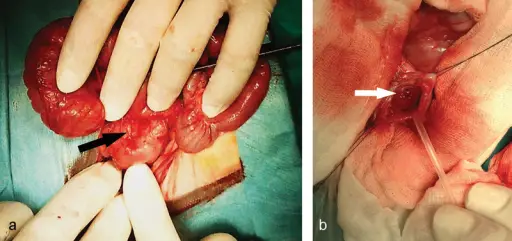
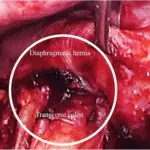
Gastrointestinal duplications are rare congenital lesions that can develop anywhere along the gastrintestinal tract. Gastrointestinal duplications may present in the newborn period as an abdominal mass. Gastrointestinal duplications may be differentiated from other intraabdominal cystic lesions by the presence of a normal gastrointestinal mucosal lining.
What is the Pathology of Gastrointestinal Duplications?
The pathology of gastrointestinal duplications is:
-Etiology: The cause of gastrointestinal duplications is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gastrointestinal duplications are unknown.
-Histology: The histology associated with gastrointestinal duplications shows duplicated gastrointestinal tissue.
How does Gastrointestinal Duplications Present?
Patients with gastrointestinal duplications typically in both males and females with before 3-years-old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gastrointestinal duplications include nausea, vomiting, obstruction, and abdominal distension. Symptoms are often specific to the location of the lesion.
How is Gastrointestinal Duplications Diagnosed?
Gastrointestinal duplications is diagnosed by computed tomography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.
How is Gastrointestinal Duplications Treated?
Gastrointestinal duplications is treated by excision. Stool softeners and enemas may improve obstructive symptoms.
What is the Prognosis of Gastrointestinal Duplications?
The prognosis of disease in lower case is fair.