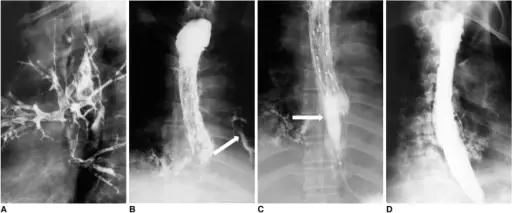
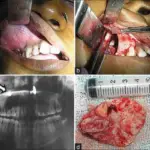
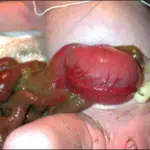
Fistulae is an abnormal connection between two body parts, such as an organ or blood vessel and another structure.
What is the Pathology of Fistulae?
The pathology of fistulae is:
-Etiology: The cause of fistulae is channel formation due to inflammation.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to fistulae is due to infection of anal crypts gland. The infection occurs in the ducts of the anal glands and the spreads resulting in an abscess. If the abscess is ruptured, a fistula may form.
-Histology: The histology associated with fistulae shows chronic inflammation, and giant cells.
How does Fistulae Present?
Patients with fistulae typically in all genders and at any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with anal fistulae include frequent anal abscesses, pain, swelling, irritation, bleeding, and fever.
How is Fistulae Diagnosed?
Fistulae is diagnosed by CT scan, MRI, anorectal ultrasound.
How is Fistulae Treated?
Fistulae is treated by fistulotomy, filling the fistula with a special glue or plug, and reconstructive surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Fistulae?
The prognosis of fistulas is fair.