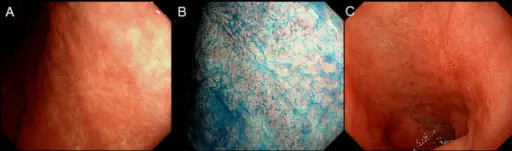
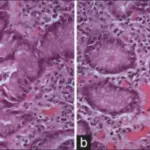
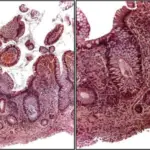
Peptic ulcer disease are open sores that develop on the inside lining of your stomach and the upper portion of your small intestine. The most common symptom of a peptic ulcer is stomach pain. Peptic ulcers include gastric ulcers that occur on the inside of the stomach.
What is the Pathology of Peptic Ulcer Disease?
The pathology of peptic ulcer disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of peptic ulcer disease are Helicobacter pylori and NSAID medications.
-Genes involved: NA.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to peptic ulcer disease are defects in the gastric or duodenal mucosa that extend through the muscularis mucosa. The epithelial cells of the stomach and duodenum secrete mucus in response to irritation of the epithelial lining and as a result of cholinergic stimulation. The superficial portion of the gastric and duodenal mucosa exists in the form of a gel layer, which is impermeable to acid and pepsin.
-Histology: The histology associated with peptic ulcer disease shows Lesions. The surface is covered with slough and inflammatory debris.
How does Peptic Ulcer Disease Present?
Patients with peptic ulcer disease typically both in male or female and present at any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with peptic ulcer disease include: burning stomach pain, feeling of fullnessbloating or belching, intolerance to fatty foods, heartburn, and nausea.
How is Peptic Ulcer Disease Diagnosed?
Peptic ulcer disease is diagnosed by endoscopy and biopsy.
How is Peptic Ulcer Disease Treated?
Peptic ulcer disease is treated by proton pump inhibitors PPI, histamine receptor blockers H2 blockers, antibiotics, and protective medications.
What is the Prognosis of Peptic Ulcer Disease?
The prognosis of peptic ulcer disease is good. The prognosis of peptic ulcer disease PUD is excellent after the underlying cause is successfully treated. Recurrence of the ulcer may be prevented by maintaining good hygiene and avoiding alcohol, smoking, and NSAIDs. Unfortunately, recurrence is common with rates exceeding 60% in most series.