Hyperplastic polyps are growth of extra cells that projects out from tissues inside your body. They occur in areas where your body has repaired damaged tissue, especially along your digestive tract. Hyperplastic colorectal polyps happen in your colon, the lining of your large intestine.
What is the Pathology of Hyperplastic Polyps?
The pathology of hyperplastic polyps is:
-Etiology: The cause of hyperplastic polyps is strongly linked with disorders that inflame or irritate the stomach, such as chronic gastritis, H. pylori gastritis, and pernicious anemia.
-Genes involved: APC gene mutations.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hyperplastic polyps are growth of extra cells that projects out from tissues inside your body. They occur in areas where your body has repaired damaged tissue, especially along your digestive tract. Hyperplastic colorectal polyps happen in your colon, the lining of your large intestine.
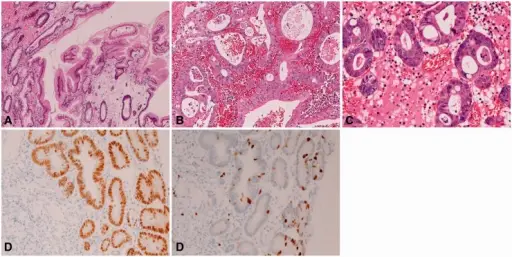
-Histology: The histology associated with hyperplastic polyps shows superficial location of maximal change, cell elongation, increase in the number and length of microvilli, accentuation of lateral intercellular interdigitations, and an increase in the breadth of basal lamina attachment.
How does Hyperplastic Polyps Present?
Patients with hyperplastic polyps typically men have a greater risk at any age but mostly over 50 years age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hyperplastic polyps include rectal bleeding, change in stool color, change in bowel habits, pan and iron deficiency anemia.
How is Hyperplastic Polyps Diagnosed?
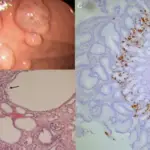
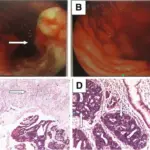
Hyperplastic polyps is diagnosed by colonoscopy, CT scan, and biopsy.
How is Hyperplastic Polyps Treated?
Hyperplastic polyps is treated by removing them during a routine endoscopic procedure, eating diet and nutritional changes.
What is the Prognosis of Hyperplastic Polyps?
The prognosis of hyperplastic polyps is good. Getting polyps removed before they become cancerous lowers your risk of developing colorectal or stomach cancer by almost 80 percent.