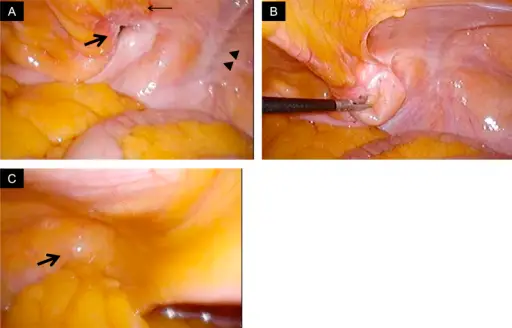
Hernias are tear in muscle or tissue that allows part of insides to bulge out. It can be a bulge of an internal organ or the intestines.
What is the Pathology of Hernias?
The pathology of hernias is:
-Etiology: The cause of hernias is a combination of pressure and an opening or weakness of muscle or fascia; the pressure pushes an organ or tissue through the opening or weak spot. Sometimes the muscle weakness is present at birth; more often, it occurs later in life.
-Genes involved: WT1, EFEMP1, EBF2 and ADAMTS6.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hernias are: It occurs as a result of the deep inguinal ring failing to close during embryogenesis after a testicle has moved through it. Once bowel or other abdominal tissue moves into and enlarges the empty space, a visible bulge forms and the hernia becomes clinically evident.
-Histology: The histology associated with hernias shows Incarceration, obstruction and strangulation.
What are the Different Types of Hernias?
Different types of hernias include:
- Epigastric hernia which occurs in the epigastric region of the abdomen above the belly button and below the rib cage.
- Femoral hernia which occurs when tissue pushes through a weak point in the groin or inner thigh.
- Hiatal hernia occurs when a person’s stomach bulges through a weak point in the diaphragm.
- Incisional hernia occurs when a person has stomach surgery. It usually involves an incision down the middle of the stomach. If the surgical wound doesn’t heal completely, that person can be more vulnerable to developing a hernia.
- Inguinal hernia occurs when a portion of intestine or fat bulges through the lower stomach wall.
- Umbilical hernia occurs when tissues in the body bulge through an area of weakness in the belly button area.
How do Hernias Present?
Patients with hernias typically men at adult life mostly but some types of hernias could develop from age 0 to 5 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hernias include: visible bulge in the affected area. Other reported symptoms include pressure, a cough, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing. Severe hernia symptoms are shooting pain, vomiting, and constipation.
How are Hernias Diagnosed?
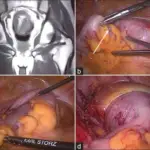
Hernias are diagnosed by physical exam, and possibly imaging tests including MRI Scans.
How are Hernias Treated?
Hernias are treated by surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Hernias?
The prognosis of hernias is excellent. They do reappear, however, in about 10 percent of adults.