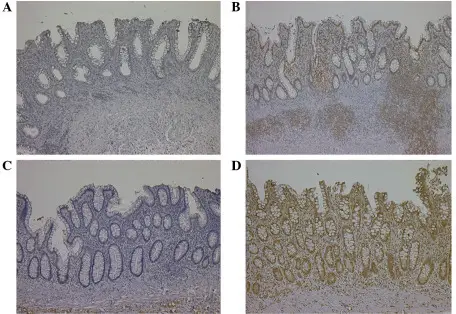
Colitis-associated neoplasia is one of the most important causes for morbidity and mortality in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases.
What is the Pathology of Colitis-Associated Neoplasia?
The pathology of disease in lower case is:
-Etiology: The cause of colitis-associated neoplasia is inflammatory bowel disease.
-Genes involved: SMAD, WNT, β-catenin.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to colitis-associated neoplasia are: Multiple processes like tumor initiation and metastasis are involved in colitis-associated neoplasia. The pathogenesis of CAC is reported to be affected by multiple pathways, including TGF-β/SMAD, WNT/β-catenin, NOD/TLR, NLRP3 inflammasome, and the cell cycle as well as apoptosis.
-Histology: The histology associated with colitis-associated neoplasia shows colonic neoplasia.
How does Colitis-Associated Neoplasia Present?
Patients with colitis-associated neoplasia typically all genders at all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with colitis-associated neoplasia include urgent bowel movements as well as cramps.
How is Colitis-Associated Neoplasia Diagnosed?
Colitis-associated neoplasia is diagnosed by sigmoidoscope, MRI, CT scan.
How is Colitis-Associated Neoplasia Treated?
Colitis-associated neoplasia is treated by drug therapy or surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Colitis-Associated Neoplasia?
The prognosis of colitis-associated neoplasia is fair.