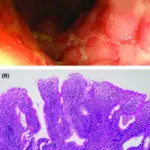
Sigmoid diverticular disease is called so because diverticula can form while straining during a bowel movement, such as with constipation. They are most common in the lower portion of the large intestine called the sigmoid colon.
What is the Pathology of Sigmoid Diverticular Disease?
The pathology of sigmoid diverticular disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of sigmoid diverticular disease is when naturally weak places in your colon give way under pressure.
-Genes involved: None.
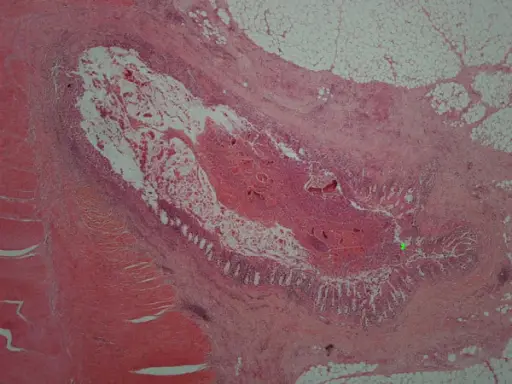
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sigmoid diverticular disease are: the obstruction of the diverticulum sac by fecalith, which by irritation of the mucosa causes low-grade inflammation, congestion and further obstruction.
-Histology: The histology associated with sigmoid diverticular disease shows structural abnormalities of colonic wall.
How does Sigmoid Diverticular Disease Present?
Patients with sigmoid diverticular disease typically in females present after 40 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sigmoid diverticular disease include: pain at lower left part of the abdomen.
How is Sigmoid Diverticular Disease Diagnosed?
Sigmoid diverticular disease is diagnosed by stool test, to rule out infection in people who have diarrhea. A CT scan, which can identify inflamed or infected pouches and confirm a diagnosis of diverticulitis. CT can also indicate the severity of diverticulitis and guide treatment.
How is Sigmoid Diverticular Disease Treated?
Sigmoid diverticular disease is treated by antibiotics to resolve bacterial infections, surgery, gentle bowel stimulation and cleansing with small aliquots of magnesium citrate, might help reduce the stool load
What is the Prognosis of Sigmoid diverticular disease?
The prognosis of sigmoid diverticular disease is good.