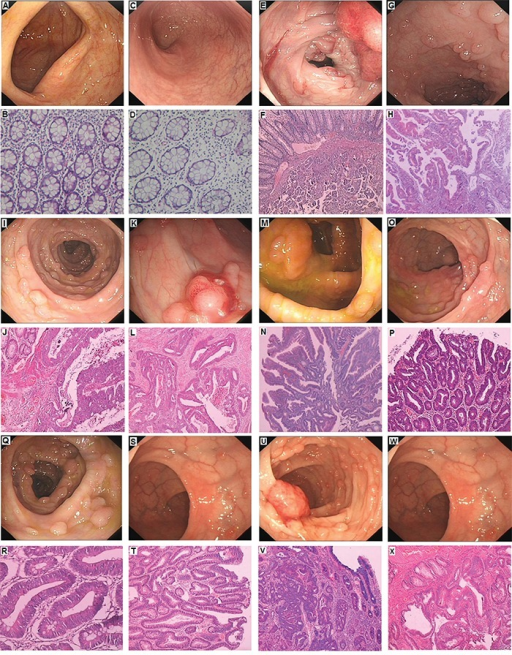
Clinical DescriptionA-B. No polyps in the colon of unaffected member with normal histology (III-2). C-D. No polyps in the rectum of unaffected member with normal histology (III-2). E-F. Polyps in the colon, Cancer invading in the submucosa in proband (III-1); G-H. Polyps of rectum showing Low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia), the gland of local lesion showing High grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in proband (III-1). I-J. Polyps of colon showing High grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-4; K-L. Polyps of rectum, adenocarcinoma in III-4. M-N. Polyps of colon is Low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia), the gland of local lesion is High grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-5; O-P. Polyps of rectum are Low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-5; Q-R. Polyps of colon are Low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-7; S-T. Polyps of rectum are Low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-7; U-V. Polyps of colon are High grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-9; W-X. Polyps of rectum are Low grade intraepithelial neoplasia (dysplasia) in III-9. A novel pathogenic large germline deletion in adenomatous polyposis coli gene in a Chinese family with familial adenomatous polyposis. Oncotarget. Not Altered. CC.
Colonic polyps are a small clump of cells that forms on the lining of the colon. Most colon polyps are harmless. But over time, some colon polyps can develop into colon cancer, which may be fatal when found in its later stages.
Examples of colonic polyps are:
- Hamartomatous polyps: juvenile polyps. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Hyperplastic polyps
- Inflammatory polyps
- Neoplastic polyps
- Adenomatous polyps