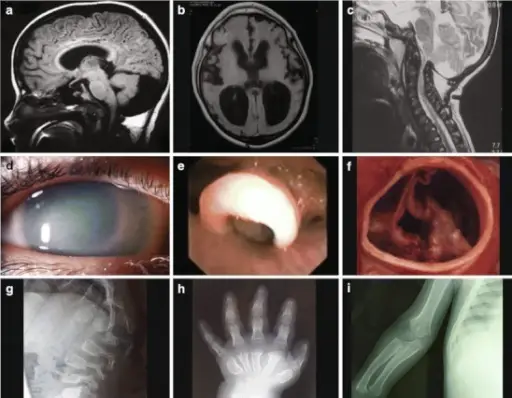
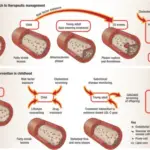
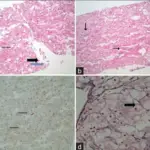
Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of over 70 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function.
Examples of lysosomal storage diseases include:
- Glycoogenosis
- Sulfatidoses
- Mucopolysaccharidoses
- Mucopolysaccharidoses
- Mucolipidoses
- Fucosidosis
- Mannosidosis
- Aspartglycosaminuria
- Wolman disease
- Acid phosphate deficiency
| Disease | Enzyme Deficiency | Major Accumulation Metabolites |
| Glycogenosis | Type 2 – Pompe disease Α-1,4-Glucosidase (lysosomal glucosidase) | Glycogen |
| Sphingolipidoses Gm1 gangliosidosis Type 1 – infantile, generalized Type 1 – juvenile Gm2 gangliosidosis Tay-Sachs disease Sandhoff disease Gm2 gangliosidosis variant AB | Gm1 ganglioside β-galactosidase Hexaminidase, α subunit Hexaminidase, β subunit Ganglioside activator protein | Gm1 ganglioside, galactose-containing oligosaccharides Gm2 ganglioside Gm2 ganglioside, globoside Gm2 ganglioside |
| Sulfatidoses Metachromatic leukodystrophy Multiple sulfatase deficiency Krabbe disease Fabry disease Gaucher disease Niemann-Pick disease | Arylsulfatase A Arylsulfatase A, B, C, steroid sulfatase; iduronate sulfatase; heparin N-sulfatase Galactocerebrosidase (galactosylceramidase) α-galactosidase A Glucocerebrosidase Sphingomyelinase | Cerebroside sulfate Sulfatide, steroid sulfate, heparin sulfate, dermatan sulfate Galactocerebroside, psychosine Ceramide trihexoside Glucocerebroside Sphingomyelin |
| Mucopolysaccharidoses Hurler syndrome Hunter syndrome | α-l-iduronidase Iduronate-2-sulfatase | Heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate Heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate |
| Mucolipidoses I-cell disease and pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy | Deficiency of phosphorylating enzymes essential for the formation of mannose-6-phosphate recognition marker; acid hydrolases lacking the recognition marker cannot be targeted to the lysosomes but are secreted extracellulary | Mucopolysaccharide, glycolipid |
| Other diseases of complex carbohydrates Fucosidosis Mannosidosis Aspartylglycosaminuria | α-Fucosidase α-Mannosidase Aspartylglycosamine amide hydrolase | Fucose-containing sphingolipids and glycoprotein fragments Mannose-containing oligosaccharides Aspartyl-2-deaxy-2-acetamido-glycosylamine |
| Other lysosomal storage disease Wolman disease Acid phosphate deficiency | Acid lipaseLysosomal acid phosphate | Cholesterol esters, triglycerides Phosphate esters |