Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis is a chronic progressive syndrome of the lungs with 3–5 years projected median survival time after diagnosis was made.
What is the Pathology of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
The pathology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is unknown.
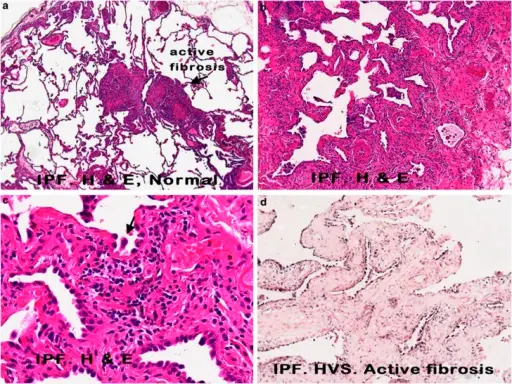
-Histology: The histology associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis shows alveolar exudate, fibrosis in the alveoli, and the interstitial septal wall with inconstant inflammation.
How does Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Present?
Patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis typically males are affected more frequently, and present at age range of 20 to 45 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis include a dry cough and slowly developing dyspnea, cor-pulmonale fingers clubbing.
How is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Diagnosed?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is diagnosed by excluding all known causes of interstitial fibrosis.
How is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is treated medical care-, pirfenidone and nintedanib antifibrotic drugs slow the lung functions weakening.
What is the Prognosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
The prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is poor, death within 6 weeks to 6 months.