Chronic bronchitis is a common chronic condition defined persistent cough with sputum for minimum of three months in at least two consecutive years not due to another cause. Typically associated with smoking.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Bronchitis?
The pathology of chronic bronchitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of chronic bronchitis is, atmospheric pollution and cigarette smoking (Most common). Other factors are genetic factors, occupation, and infection.
-Genes involved: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen (CTLA) 4.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to chronic bronchitis results from a succession of occurrences of acute bronchitis.
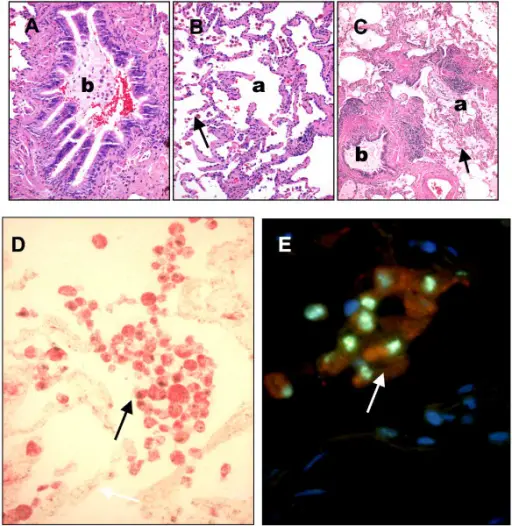
-Histology: The histology associated with chronic bronchitis shows increased Reid index, epithelium show squamous metaplasia and dysplasia, and little inflammatory cell infiltrate.
How does Chronic Bronchitis Present?
Patients with chronic bronchitis typically affect males more compared to females present at age range of >50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with chronic bronchitis include Cough, sputum production, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, fever general malaise, and chest pain.
How is Chronic Bronchitis Diagnosed?
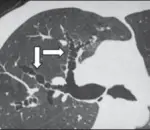
Chronic bronchitis is diagnosed through history taking (persistent cough with expectoration on most days for at least three months of the year for two or more consecutive years), cultures, and staining for influenza virus. Imaging studies, chest radiography, and bronchoscopy may also be useful.
How is Chronic Bronchitis Treated?
Chronic bronchitis is treated through symptom and episodic infection treatment, environmental changes.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Bronchitis?
The prognosis of chronic bronchitis is good.