Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease is a syndrome of the small airway of well-organized lesions found in the lungs of those who smoke.
What is the Pathology of Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease?
The pathology of respiratory bronchiolitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease is smoking, exposure to toxic fumes.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease are unknown.
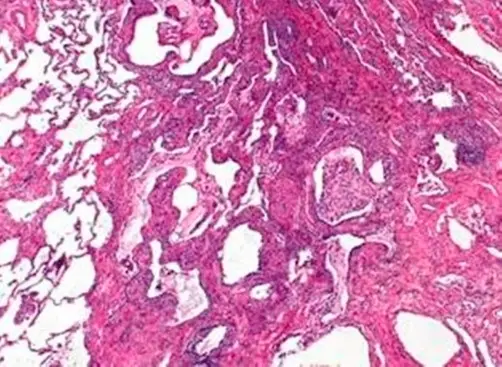
-Histology: The histology associated with bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease shows yellow to light brown and finely defined granular cytoplasmic pigments.
How does Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Present?
Patients with respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease typically are from both genders in the age of between 30-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with include respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease is dyspnea, obstructive and restrictive pulmonary signs, cough, and tiredness.
How is Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosed?
Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease is diagnosed through imaging chest radiography and high-resolution computed topography, clinically using the presenting symptoms.
How is Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Treated?
Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease is treated mostly and effectively by encouraging cessation of smoking and also con current use of corticosteroids and immunosuppressives.
What is the Prognosis of Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease?
The prognosis of respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease is good. This is because those with the disease have a higher and prolonged survival rate.