Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is a range of immunologically arbitrated, predominantly interstitial, lung ailments caused by intense, and prolonged contact to inhaled organic specks of dust and related job-related antigens.
What is the Pathology of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
The pathology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of hypersensitivity pneumonitis is reactivity to an antigen which include, thermoactinomyces sacchari, avian or animal proteins, saccharopolyspora rectivirgula among others.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hypersensitivity pneumonitis are partly understood. Thought to happen chiefly through type III hypersensitivity response for acute hypersensitivity. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis is believed to be a result of type IV, T-cell mediated responses.
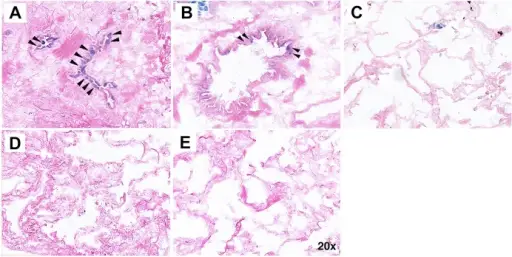
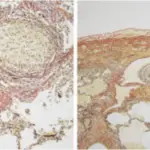
-Histology: The histology associated with hypersensitivity pneumonitis shows interstitial pneumonitis entailing lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages. Noncaseating granulomas, interstitial fibrosis, and obliterative bronchiolitis may also be seen.
How does Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Present?
Patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis typically males are more affected than females present at age range of 40 to60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hypersensitivity pneumonitis include episodes of fever, dyspnea, cough, and leukocytosis. On chest radiograph, diffuse and nodular infiltrates appear.
How is Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Diagnosed?
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is diagnosed through physical and history examination, Imaging- Chest radiograph and CT scan display radiographic indication. Bronchoscopic alveolar lavage displays an indication of lymphocytic predominance.
How is Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Treated?
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is treated through antigen avoidance, medical care- corticosteroid therapy, antihistamines, bronchodilators, and cromolyn sodium.
What is the Prognosis of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
The prognosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis is poor especially on an indication of pulmonary fibrosis.