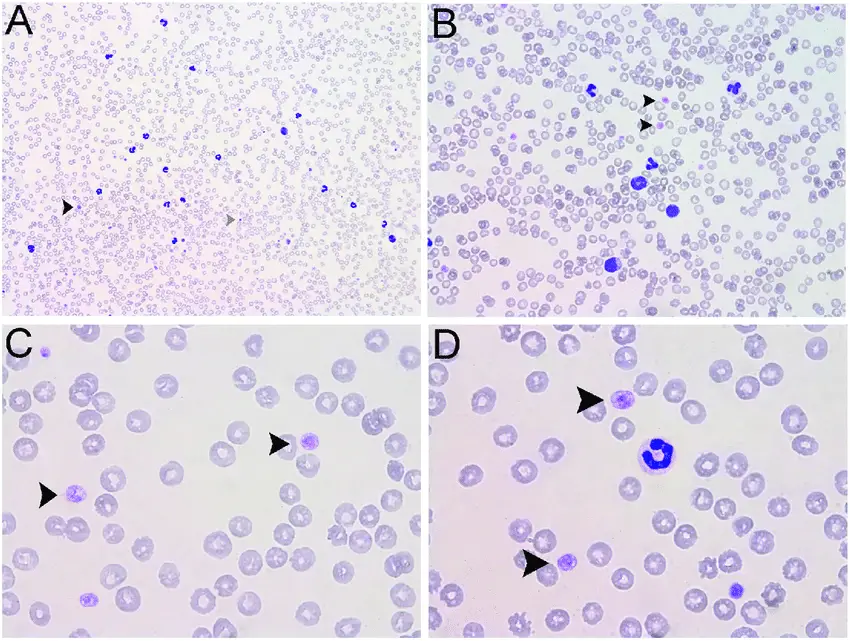
Bernard-Soulier syndrome is a bleeding disorder associated with abnormal platelets.
What is the Pathology of Bernard-Soulier Syndrome?
The pathology of Bernard-Soulier syndrome is:
-Etiology: The cause of Bernard-Soulier syndrome is the genetic mutations in one of the Gp1b complex genes.
-Genes involved: GP1BA, GP1BB, or GP9.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Bernard-Soulier syndrome is the proteins produced from GP1BA, and GP1BB.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome shows thrombocytopenia, giant platelets, and qualitative platelet defects resulting in bleeding tendency.
How does Bernard-Soulier Syndrome Present?
Patients with Bernard-Soulier syndrome typically are either male or female present at the age range of infants. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome include easy bruising and nosebleeds.
How is Bernard-Soulier Syndrome Diagnosed?
Bernard-Soulier syndrome is diagnosed with blood and platelets tests.
How is Bernard-Soulier Syndrome Treated?
Bernard-Soulier syndrome is treated with platelet transfusion as needed.
What is the Prognosis of Bernard-Soulier Syndrome?
The prognosis of Bernard-Soulier syndrome is fair.