Qualitative platelet disorders is a disorder affecting the structure or function of platelets.
What is the Pathology of Qualitative Platelet Disorders?
The pathology of qualitative platelet disorders is:
-Etiology: The cause of qualitative platelet disorders is von Willebrand disease or absence of thrombocytopenia.
-Genes involved: None.
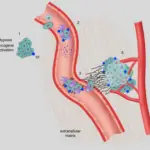
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to qualitative platelet disorders includes deficiency or abnormality in the platelet granules or their contents also known as a storage pool disorder.
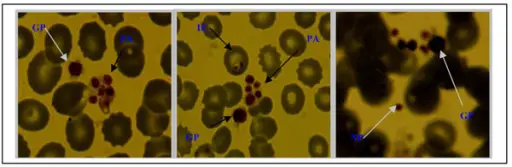
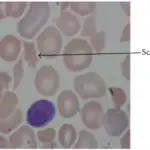
-Histology: The histology associated with qualitative platelet disorders shows the cytoplasmic granules, platelet membranes, and the cytoskeleton.
How does Qualitative Platelet Disorders Present?
Patients with qualitative platelet disorders typically affect both males and females present at the age range of 3-50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with qualitative platelet disorders include easy bruising, nosebleeds, bleeding of the mouth or gums, heavy menstrual bleeding, postpartum (after childbirth) bleeding, bleeding following dental work, and bleeding with invasive surgical procedures.
How is Qualitative Platelet Disorders Diagnosed?
Qualitative platelet disorders is diagnosed using blood tests.
How is Qualitative Platelet Disorders Treated?
Qualitative platelet disorders is treated with platelet transfusions or plasma exchange along with medications.
What is the Prognosis of Qualitative Platelet Disorders?
The prognosis of qualitative platelet disorders is poor with an increased mortality rate.