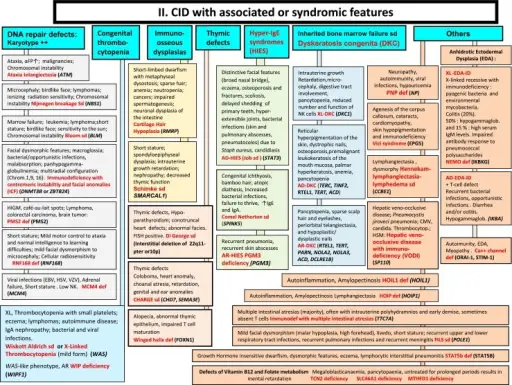
CID with associated or syndromic features. These syndromes are generally associated with T-cell immunodeficiency. αFP alpha- fetoprotein, AD Autosomal Dominant inheritance, AR Autosomal Recessive inheritance, CMF Flow cytometry available, EDA Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, EDA-ID Anhidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Immunodeficiency, FILS Facial dysmorphism, immunodeficiency, livedo, and short stature, FISH Fluorescence in situ Hybridization, HSM Hepatosplenomegaly, HSV Herpes simplex virus, Ig Immunoglobulin, VZV Varicella Zoster virus, WAS Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, XL X-Linked inheritance. The 2015 IUIS Phenotypic Classification for Primary Immunodeficiencies. Bousfiha A, Jeddane L, Al-Herz W, Ailal F, Casanova JL, Chatila T, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Franco JL, Gaspar HB, Holland SM, Klein C, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Oksenhendler E, Picard C, Puck JM, Sullivan KE, Tang ML - Journal of clinical immunology (2015). Not Altered. CC.
Immunodeficiency disorders are those which impair the immune system’s ability to defend the body against foreign or abnormal cells that invade or attack it such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and cancer cells.
Immunodeficiency disorders include primary immunodeficiencies, defects in innate immunity, defects in adaptive immunity, defects in lymphocyte maturation, defects in lymphocyte activation and function, immunodeficiencies associated with systemic diseases, secondary immunodeficiencies, amyloidosis, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).