Mycobacterium avium complex is a group of bacteria related to tuberculosis. These germs are very common in food, water, and soil.
What is the Pathology of Mycobacterium Avium Complex?
The pathology of mycobacterium avium complex is:
-Etiology: The cause of mycobacterium avium complex is Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellular.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to mycobacterium avium complex are: the bacteria spreads through the submucosal tissue, lymphatic drainage transports mycobacteria to abdominal lymph nodes, from which the organisms enter the bloodstream, from where the hematogenous spread occurs to many sites such as spleen, bone marrow, and liver.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with mycobacterium avium complex shows strains that are known to exhibit variation in colony morphology. In addition to the smooth transparent, smooth opaque, and rough opaque.
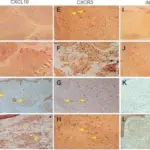
-Histology: The histology associated with mycobacterium avium complex shows necrotizing and non necrotizing granulomas and positive AFB smear results.
How does Mycobacterium Avium Complex Present?
Patients with mycobacterium avium complex typically are all genders of all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with mycobacterium avium complex include shortness of breath, abdominal pain, anemia, fatigue, diarrhea, sweating, and weight loss.
How is Mycobacterium Avium Complex Diagnosed?
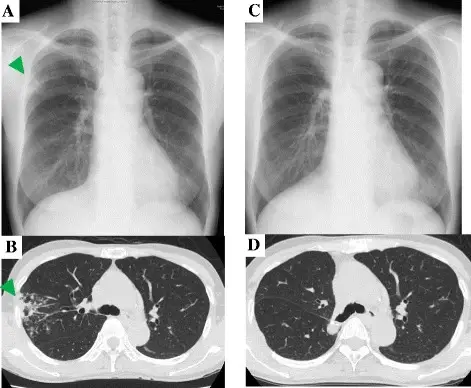
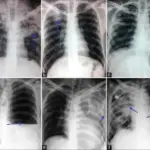
Mycobacterium avium complex is diagnosed by x-rays or CT scan.
How is Mycobacterium Avium Complex Treated?
Mycobacterium avium complex is treated by antimicrobials.
What is the Prognosis of Mycobacterium Avium Complex?
The prognosis of mycobacterium avium complex is good.