Suppurative arthritis is an infection in the synovial fluid and joint tissues.
What is the Pathology of Suppurative Arthritis?
The pathology of suppurative arthritis is:
-Etiology: The cause of suppurative arthritis is a bacterial infection.
-Genes involved: None.
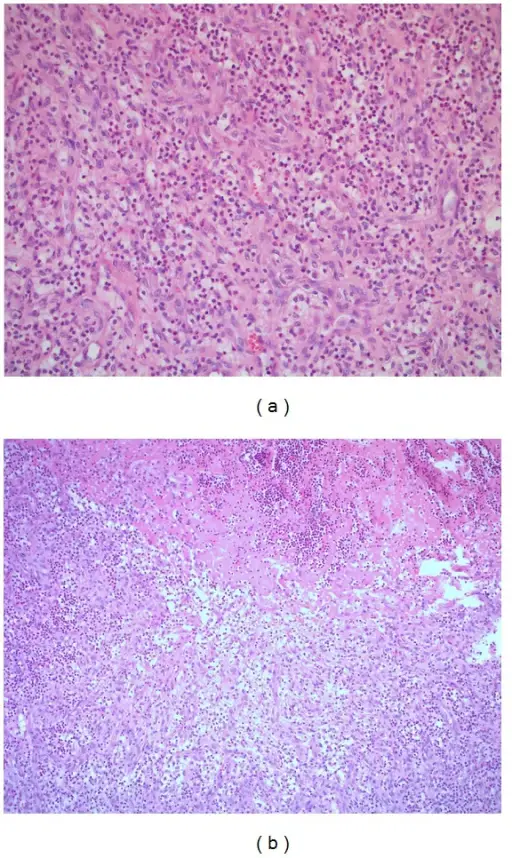
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to suppurative arthritis includes seeding of the joint with bacteria, most commonly Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, or gram-negative rods. Syphilis may also cause suppurative arthritis.
-Histology: The histology associated with suppurative arthritis shows neutrophils and bacteria.
How does Suppurative Arthritis Present?
Patients with suppurative arthritis are typically either male or female. The clinical features include extreme pain, chills. fatigue and generalized weakness, fever, and inability to move the affected joint.
How is Suppurative Arthritis Diagnosed?
Suppurative arthritis diagnosis is made by analysis of fluid that has been removed from the joint, including microscopic examination and culture.
How is Suppurative Arthritis Treated?
Suppurative arthritis requires drainage of the joint and antibiotics, usually intravenously administered.
What is the Prognosis of Suppurative Arthritis?
The prognosis of suppurative arthritis is fair if treated in a timely manner.