Synovial cysts are abnormal fluid-filled sacs in joints in the spine.
What is the Pathology of Synovial Cysts?
The pathology of synovial cysts is:
-Etiology: The cause of synovial cysts is a result of degenerative changes associated with aging.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to synovial cysts remains unclear.
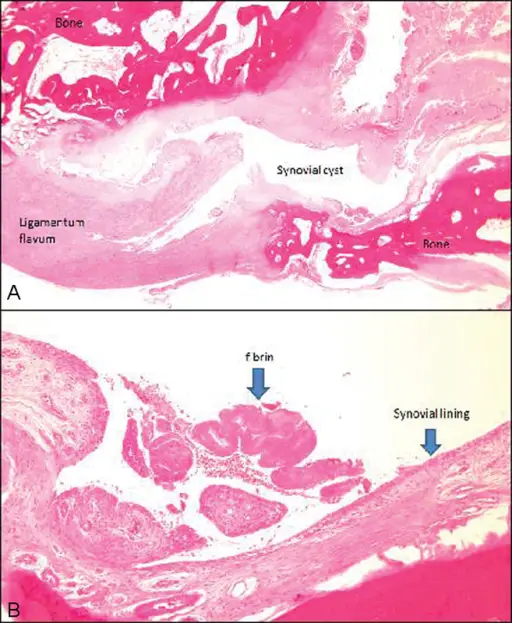
-Histology: The histology associated with synovial cysts shows pseudocysts and degenerative changes. There may be granular calcifications and a foreign body giant cell reaction.
How do Synovial Cysts Present?
Patients with synovial cysts are typically males or females over 65 years old. Symptoms depend on the size and location of the cyst, but are typically only a nodule and milde pressure discomfort.
How are Synovial Cysts Diagnosed?
Synovial cysts are diagnosed using X-ray and MRI.
How are Synovial Cysts Treated?
Synovial cysts are treated with pain medication and seeking physical therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Synovial Cysts?
The prognosis of synovial cysts is fair. The symptoms and level of pain or discomfort may remain stable for many years.