Postinfectious glomerulonephritis is a disease of the glomeruli that results after the effects of an infection.
What is the Pathology of Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis?
The pathology of postinfectious glomerulonephritis is the study of the effects of infection occurring in other parts that affects the glomeruli.
-Etiology: The cause of postinfectious glomerulonephritis is bacterial infection in other body parts.
-Genes involved: None.
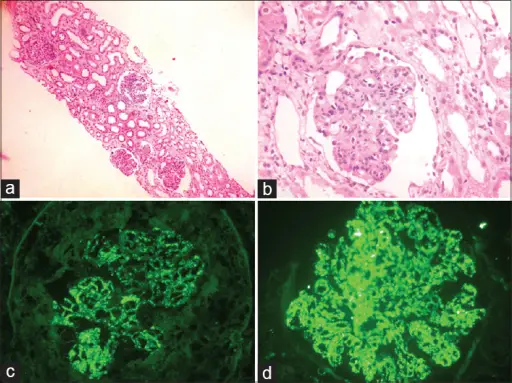
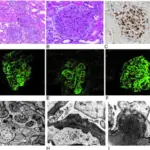
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to postinfectious glomerulonephritis during the disease process, antibodies, antigens and the complement system are responsible to fight infection. In this disease those immune complexes get trapped in the kidney filters hindering them from filtering normally causing glomerulonephritis.
-Morphology: Not applicable.
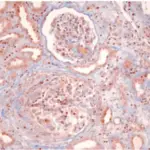
-Histology: The histology associated with postinfectious glomerulonephritis shows larger glomeruli cells, increased inflammatory cells, hump-like subendothelial immune complex deposits.
How does Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis Present?
Patients with postinfectious glomerulonephritis typically are females present at the the age range of 6-10 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with postinfectious glomerulonephritis include generalized edema of all parts of the body including g the face, hypertension, coca-cola coloured urine, oliguria, joint pain and stiffness.
How is Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis Diagnosed?
Postinfectious glomerulonephritis is diagnosed through physical examination, auscultation, blood tests, urinalysis, kidney biopsy.
How is Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis Treated?
Postinfectious glomerulonephritis is treated by mainly managing the symptoms, blood pressure regulation, and salt restriction.
What is the Prognosis of Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis?
The prognosis of postinfectious glomerulonephritis is goodsince it resolves after the infection is treated.