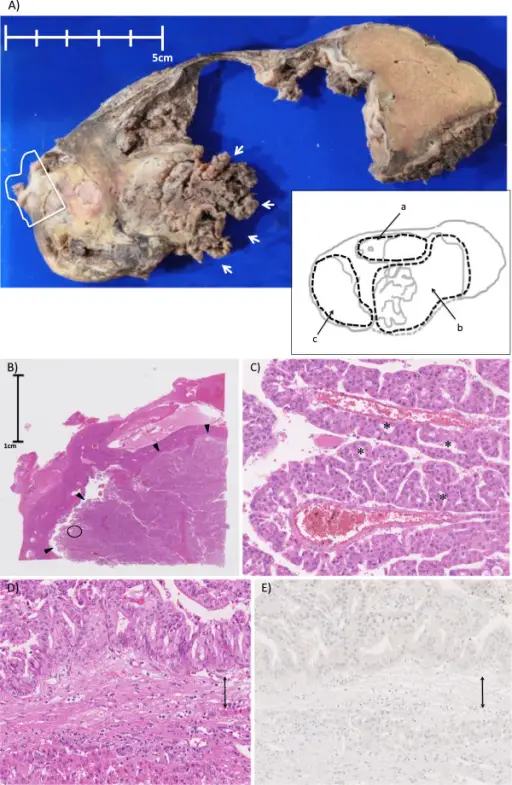
(A) The gross appearance of the tumor. Macroscopically, the whole lesion was 130 x 90 mm in size in the resected specimen. The image of the lesion is illustrated as an inset in the lower right. The letters (a), (b), and (c) denote separated cystic lesions and correspond to those in Figure 1B. The medial side of the cyst wall of the cyst (b) and the septum between the cysts (a) and (b) are lost in the specimen. There is a papillary mass in the posterior side of the lesion (b) (indicated by arrows). The lesion (c) is filled with solid components. (B) A loupe observation of the solid component surrounded by a white line in (A) (hematoxylin and eosin). A papillary nodular mass (indicated by arrowheads) is seen inside the cyst wall. (C) A magnified observation of the point encircled in (B) (x20, hematoxylin, and eosin). Arborizing papillae with thin-walled vessel are seen. The lesion is lined by multilayers of cuboidal to columnar cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm forming intraepithelial lumina (some of the lumens are indicated by asterisks (*)). The tumor cells had sufficient cytoarchitectural atypia to be classified as having high-grade dysplasia. (D) (E) A magnified (x20) image of the cyst wall (hematoxylin and eosin in (D)) and immunohistochemical staining for progesterone receptor in (E). The cyst wall is indicated by a double arrow. Tumor components consisting of multilayer cuboidal to columnar cells (upper side of the cystic wall in the picture, inside of the tumor) and normal hepatocytes (lower side of the cystic wall in the picture, outside of the tumor) are seen. No ovarian-like stromata were seen throughout the cyst walls. Cystic tumor of the liver without ovarian-like stroma or bile duct communication: two case reports and a review of the literature: Kishida N, Shinoda M, Masugi Y, Itano O, Fujii-Nishimura Y, Ueno A, Kitago M, Hibi T, Abe Y, Yagi H, Tanimoto A, Tanabe M, Sakamaoto M, Kitagawa Y - World journal of surgical oncology (2014). Not altered. CC.
Tumors of the liver are malignancies that originate or metastasize to the liver.
Tumors of the liver include:
- Nodular hyperplasias
- Hepatocellular adenomas
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Hepatoblastoma
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metastasis
