Nodular hyperplasias of the liver are the benign tumors of the liver.
What is the Pathology of Nodular Hyperplasias of the Liver?
The pathology of nodular hyperplasias of the liver is:
-Etiology: The cause of nodular hyperplasias of the liver is the increased hepatocyte number caused by hypoperfusion or hyperperfusion from anomalous arteries within the hepatic lobule.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
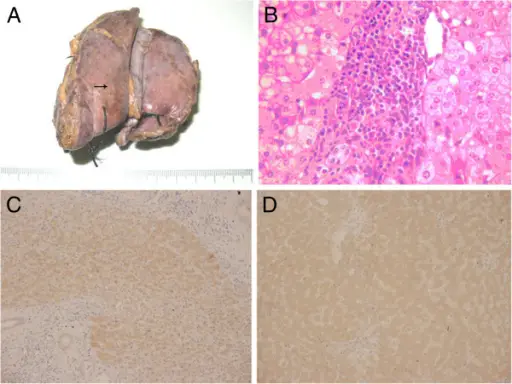
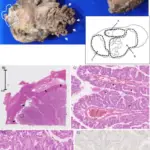
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to nodular hyperplasias of the liver is unknown, however, it is characterized by a well-circumscribed region of hyperplastic liver parenchyma containing a stellate fibrous scar.
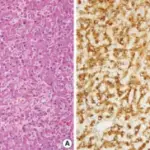
-Histology: The histology associated with nodular hyperplasias of the liver shows hyperplastic hepatocytes.
How does Nodular Hyperplasias of the Liver Present?
Patients with nodular hyperplasias of the liver typically affect young women present at the age range of 20-35. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with nodular hyperplasias of the liver include a lump or pain in the stomach. However, most are asymptomatic.
How is Nodular Hyperplasias of the Liver Diagnosed?
Nodular hyperplasias of the liver is diagnosed through CT scan, MRI, tumor markers, and biopsy.
How is Nodular Hyperplasias of the Liver Treated?
Nodular hyperplasias of the liver is treated through surgical resection or hepatectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Nodular Hyperplasias of the Liver?
The prognosis of nodular hyperplasias of the liver is good if treated early and promptly.