Hepatocellular carcinoma is the primary malignancy of the liver with hepatocellular differentiation.
What is the Pathology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
The pathology of hepatocellular carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of hepatocellular carcinoma may be cirrhosis, infections, hepatitis B & C, and metabolic disorders.
-Genes involved: HFE.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to hepatocellular carcinoma include low grade dysplasia that progresses to carcinoma.
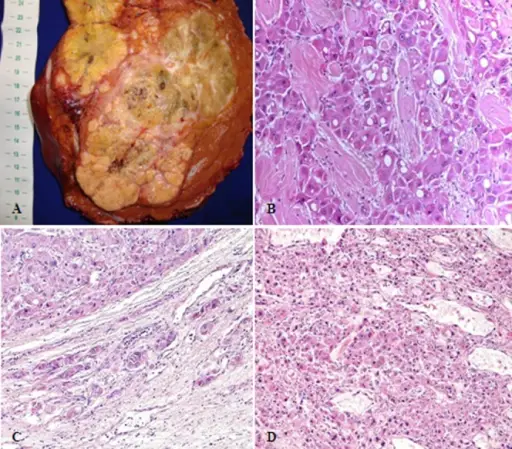
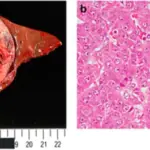
-Histology: The histology associated with hepatocellular carcinoma shows a well-circumscribed mass that appears tan-yellow to green.
How does Hepatocellular Carcinoma Present?
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma typically affect males present at the age range of 28-65 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with hepatocellular carcinoma include abdominal pain, weight loss, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly, jaundice, ascites.
How is Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is diagnosed using ultrasound, CT, and MRI, fine needle aspiration, and biopsy.
How is Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is treated using surgical intervention, ablation therapy, and systemic therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
The prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma is poor with a 5-year survival rate of 20%.